Zynamite PX

Zynamite PX
Zynamite® : Boosting mental and physical energy - Innovative, award winning and studied: Energy, Mental and Sports Performance, Nootropic …
Zynamite® is the patented extract of Nektium from the mango leaf Mangifera indica, standardized in mangiferin (Mangifera indica is in the BelFrIt list), launched at Vitafoods 2018..Zynamite® provides sustained mental and physical energy and concentration without negative side effects (anxiety, nervousness, heartbeat, blood pressure), even providing better results than caffeine..He obtained the first Nutraingredients 2018 and 2019 prize, and twice ESSNA awards (Best free from product and Game Changer in sport nutrition), e-gaming 2020..Zynamite has been studied in-vivo & in clinical studies : 8 internal studies including 6 clinical studies and toxicology study. Some initial studies also show the possible total replacement of caffeine, avoiding the caffeine crash..Different grades are available :- Zynamite® 60 : the original extract, providing 60% Mangiferin
- Zynamite® PX : a combination of Zynamite® and quercetin, for sport
- Zynamite® 15WS (previously named Zynamite®+) : the aqueous extract, soluble, with even improved bio-availability
Zynamite® PX is a ready-to-use combination of Zynamite 60% + Quercetin from Sophora japonica specially developed to improve sports performance.
The effect of Zynamite® on performance is also tested in sports formulations, 4 clinical studies focused on the sports axis and showed the following effects:
- Improved VO2 max and maximum power output (incl. after ischemia)
- Preservation of muscle function
- Improved exercise performance
- Decreased muscle damage and pain
- Accelerate muscle recovery
- Better cerebral oxygenation
Zynamite® does not cause arrhythmia or change blood pressure.
The recommended dose (based on studies) is 420 mg / day of Zynamite® PX (i.e. 140 mg of Zynamite® and 280 mg of Sophora j. 50% quercetin)
Suitable for sports powder and gel products.
Mango - Extracts from fruits or leaves of the mango tree
Mangifera indica, the common mango tree, is widely cultivated in the tropics and subtropics of the world. Mango leaf infusions and decoctions have been used in traditional healthcare systems and have been known for centuries for their health benefits. The properties of mango leaves range from the anti-inflammatory potential to the regulation of fats and sugars in the blood, including anti-oxidant, antiviral, cardiotonic, hypertensive and anti-inflammatory (COX-2 inhibitor and decreased release of cytokines).

The award-winning ingredient that delivers enhanced mental energy and improved sports performance
|
 |

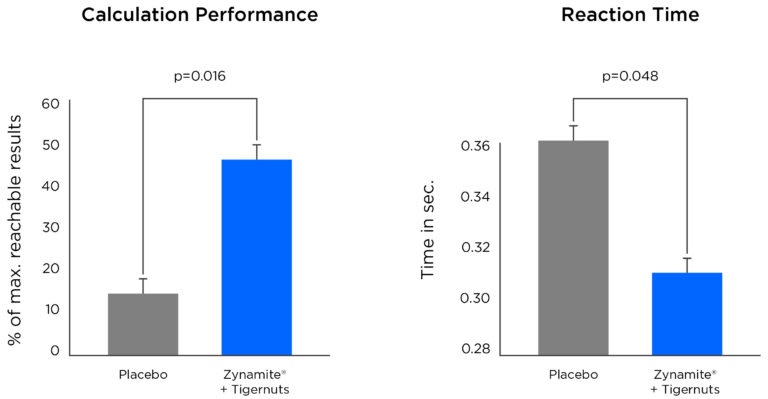
Nootropic activitiesCognitive / Mood |
 |
Zynamite is an ingredient that enhances mental energy. Clinical studies of formulations containing Zynamite point to rapid onset of enhanced brain electrical activity, with statistically significant improvement in reaction time and calculation performance.
-
Activates brain electrical activity
-
Increases long term potentiation
-
Faster reaction time and increased calculation performance
-
Decreased fatigue
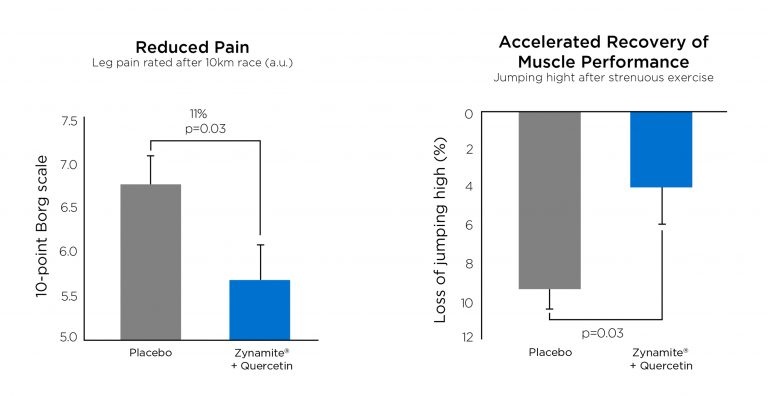
Sports performanceSport recovery |
 |
The effect on pain and recovery was studied after a 10km race followed by 100 drop jumps, demonstrating the following results:
-
Accelerated recovery of muscle performance
-
Reduced pain and muscle damage elicited by competitive exercise
Tested in repeat sprint exercise as well as exercise during simulated exhaustion (ischaemia-reperfusion model) in men and women.
-
Increased peak power output
-
Increased mean power output
-
Increased VO2max
-
Increased brain oxygenation in women
-
Increased muscle oxygen extraction
-
Decreased lactate
Zynamite® is an ingredient that delivers mental energy and supports the mental and physical aspects of sports performance. Clinical studies of formulations containing Zynamite® significantly improves both peak power output and mean power output in fatigued and exhausted men and women – that place where athletes find themselves when they need your help the most.
Faster reaction and quicker adaptation to changing conditions are essential to high performance athletics. The cognitive benefits of Zynamite® combined with the physical make this ingredient a unique solution for athletes, e-sports, shift workers, truck drivers and every person in need of mental and physical energy.
Intriguingly, in vivo studies of Zynamite® have pointed to the potential for synergies between Zynamite® and low doses of caffeine, suggesting that formulations that combine these ingredients will be attractive to consumers. This sets up exciting formulating options that include both ‘stim’ and ‘non-stim’ products.
-
Studies & Documents(16)
-
News(8)
Zynamite® enhance sport Performances, brain oxygenation and muscle extraction of oxygen
Supplementation with the combination of two botanical extracts of mangiferin and luteolin enhances exercise sprint performance, likely by improving brain oxygenation and allowing a higher muscle extraction of oxygen. These effects were observed following 48 h and 15 days of supplementation without significant differences between the two doses tested.
Abstrat : The natural polyphenols mangiferin and luteolin have free radical-scavenging properties, induce the antioxidant gene program and down-regulate the expression of superoxide-producing enzymes. However, the effects of these two polyphenols on exercise capacity remains mostly unknown. To determine whether a combination of luteolin (peanut husk extract containing 95% luteolin, PHE) and mangiferin (mango leave extract (MLE), Zynamite®) at low (PHE: 50 mg/day; and 140 mg/day of MLE containing 100 mg of mangiferin; L) and high doses (PHE: 100 mg/day; MLE: 420 mg/day; H) may enhance exercise performance, twelve physically active men performed incremental exercise to exhaustion, followed by sprint and endurance exercise after 48 h (acute effects) and 15 days of supplementation (prolonged effects) with polyphenols or placebo, following a double-blind crossover design. During sprint exercise, mangiferin + luteolin supplementation enhanced exercise performance, facilitated muscle oxygen extraction, and improved brain oxygenation, without increasing the VO2. Compared to placebo, mangiferin + luteolin increased muscle O2 extraction during post-exercise ischemia, and improved sprint performance after ischemia-reperfusion likely by increasing glycolytic energy production, as reflected by higher blood lactate concentrations after the sprints. Similar responses were elicited by the two doses tested. In conclusion, acute and prolonged supplementation with mangiferin combined with luteolin enhances performance, muscle O2 extraction, and brain oxygenation during sprint exercise, at high and low doses.
In conclusion : Supplementation with the combination of two botanical extracts of mangiferin and luteolin enhances exercise sprint performance, likely by improving brain oxygenation and allowing a higher muscle extraction of oxygen. These effects were observed following 48 h and 15 days of supplementation without significant differences between the two doses tested.
Keywords: sports nutrition; ergogenic aids; polyphenols; performance; O2 extraction; ischemia; reperfusion; metabolism; exercise
Enhancement of Exercise Performance by 48 Hours, and 15-Day Supplementation with Mangiferin and Luteolin in Men - Miriam Gelabert-Rebato [Nektium], Julia C. Wiebe [Nektium], Marcos Martin-Rincon, Victor Galvan-Alvarez, David Curtelin, Mario Perez-Valera, Julian Juan Habib, Alberto Pérez-López, Tanausú Vega, David Morales-Alamo and Jose A L Calbet, 6 February 2019 Nutrients 2019, 11, 344
Zynamite increases VO2peak and Peak Power Output, and Preserves Skeletal Muscle Function [Sport]
this study shows that the MLE 60% mangiferin (Zynamite) has a remarkable ergogenic effect increasing muscle power in fatigued subjects, without increasing the consumption of oxygen, submaximal exercise efficiency or submaximal and maximal blood lactate concentrations. This type of response is expected for a compound acting on the central nervous system. We have also shown for the first time in humans that MLE combined with quercetin and tiger nut extract assist in maintaining skeletal muscle function during ischemia/reperfusion, strongly suggesting that this combination is also acting directly on the skeletal muscles. Further studies should explore whether MLE/quercetin/tiger nut extract might have clinical application to prevent ischemia-reperfusion damage in patients during surgery or after post-embolism reperfusions.
Abstract : It remains unknown whether polyphenols such as luteolin (Lut), mangiferin and quercetin (Q) have ergogenic effects during repeated all-out prolonged sprints. Here we tested the effect of Mangifera indica L. leaf extract (MLE) rich in mangiferin (Zynamite®) administered with either quercetin (Q) and tiger nut extract (TNE), or with luteolin (Lut) on sprint performance and recovery from ischemia-reperfusion. Thirty young volunteers were randomly assigned to three treatments 48 h before exercise. Treatment A: placebo (500mg of maltodextrin/day); B: 140mg of MLE (60% mangiferin) and 50mg of Lut/day; and C: 140mg of MLE, 600mg of Q and 350mg of TNE/day.
After warm-up, subjects performed two 30 s Wingate tests and a 60 s all-out sprint interspaced by 4min recovery periods. At the end of the 60 s sprint the circulation of both legs was instantaneously occluded for 20 s. Then, the circulation was re-opened and a 15 s sprint performed, followed by 10 s recovery with open circulation, and another 15 s final sprint. MLE supplements enhanced peak (Wpeak) and mean (Wmean) power output by 5.0–7.0% (P < 0.01). After ischemia, MLE+Q+TNE increased Wpeak by 19.4 and 10.2% compared with the placebo (P < 0.001) and MLE+Lut (P < 0.05), respectively. MLE+Q+TNE increased Wmean post-ischemia by 11.2 and 6.7% compared with the placebo (P < 0.001) and MLE+Lut (P = 0.012). Mean VO2 during the sprints was unchanged, suggesting increased efficiency or recruitment of the anaerobic capacity after MLE ingestion. In women, peak VO2 during the repeated sprints was 5.8% greater after the administration of MLE, coinciding with better brain oxygenation. MLE attenuated the metaboreflex hyperpneic response post-ischemia, may have improved O2 extraction by the Vastus Lateralis (MLE+Q+TNE vs. placebo, P = 0.056), and reduced pain during ischemia (P = 0.068). Blood lactate, acid-base balance, and plasma electrolytes responses were not altered by the supplements. In conclusion, a MLE extract rich in mangiferin combined with either quercetin and tiger nut extract or luteolin exerts a remarkable ergogenic effect, increasing muscle power in fatigued subjects and enhancing peak VO2 and brain oxygenation in women during prolonged sprinting. Importantly, the combination of MLE+Q+TNE improves skeletal muscle contractile function during ischemia/reperfusion.
Conclusion (partial) : this study shows that the MLE 60% mangiferin (Zynamite) has a remarkable ergogenic effect increasing muscle power in fatigued subjects, without increasing the consumption of oxygen, submaximal exercise efficiency or submaximal and maximal blood lactate concentrations. This type of response is expected for a compound acting on the central nervous system. We have also shown for the first time in humans that MLE combined with quercetin and tiger nut extract assist in maintaining skeletal muscle function during ischemia/reperfusion, strongly suggesting that this combination is also acting directly on the skeletal muscles. Further studies should explore whether MLE/quercetin/tiger nut extract might have clinical application to prevent ischemia-reperfusion damage in patients during surgery or after post-embolism reperfusions.
Keywords: sprint exercise, polyphenols, antioxidants, fatigue, recovery
Mangifera indica L. Leaf Extract in Combination With Luteolin or Quercetin Enhances VO2peak and Peak Power Output, and Preserves Skeletal Muscle Function During Ischemia-Reperfusion in Humans - Miriam Gelabert-Rebato, Julia C. Wiebe, Marcos Martin-Rincon, Nigel Gericke, Mario Perez-Valera, David Curtelin, Victor Galvan-Alvarez, Laura Lopez-Rios, David Morales-Alamo and Jose A. L. Calbet
Central nervous system activities of Zynamite - nootropic innovation
While the translational clinical trials of MLE are limited by being single dose studies in a small number of subjects, they provide the first clinical evidence that the extract is well tolerated with no cardiovascular sideeffects, can induce changes in brain electrical activity, may give a faster reaction time, and decrease fatigue. These CNS activities support the reported folk-uses use of mango leaf tea as a substitute for tea and as a traditional remedy for fatigue and exhaustion. Extract Mangifera indica L., Zynamite, has nootropic potential, and larger clinical studies are needed to realise this potential.
Abstract : Ethnobotanical relevance: Leaves of Mangifera indica L. have folk-uses in tropical regions of the world as health teas, as a remedy for exhaustion and fatigue, as a vegetable, and as a medicine. Mangifera indica leaf extract (MLE) had previously been demonstrated to alter brain electrical activity in-vivo. The aim of the present series of studies was to investigate whether mangiferin, a major compound in leaves and in MLE, is responsible for the neurocognitive activity of MLE, and if the CNS activities of MLE have translational potential.
Materials and methods: MLE, tradename Zynamite, is produced by Nektium Pharma, Spain. Isolated mangiferin was tested in-vitro in radioligand binding and enzyme inhibition studies against 106 CNS targets. Changes in the electroencephalograms (EEG’s) of MLE and mangiferin were recorded in-vivo from four brain regions. Two double blind randomized placebo-controlled crossover clinical trials were conducted, each with 16 subjects. At 90 min and at 60 min respectively, after oral intake of 500 mg MLE, EEG recordings, psychometric tests, mood state, and tolerability were studied.
Results: Isolated mangiferin is a selective inhibitor of catechol- O -methyltransferase (COMT) with an IC50 of 1.1 μM, with no activity on the CNS targets of caffeine. Both mangiferin and MLE induce similar changes in longterm potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus in-vitro, and induce a similar pattern of EEG changes in-vivo. In both translational clinical trials MLE was well tolerated, with no cardiovascular side-effects. In both studies MLE caused significant spectral changes in brain electrical activity in cortical regions during cognitive challenges, different to the attenuated spectral changes induced by caffeine. There were no significant changes in the psychometric tests other than reaction time for all groups. In the second study there was a trend to faster reaction time within group for MLE (p = 0.066) and the percentage improvement in reaction time for MLE compared to placebo was significant (p = 0.049). In the first study MLE improved all scores for Profile of Mood States (POMS), with the score for “fatigue” significantly improved (p = 0.015); in the second study the POMS score for “dejection” was improved in the caffeine group, p = 0.05.
Mangiferin is a COMT inhibitor of moderate potency and is the major CNS-active compound in MLE. Both mangiferin and MLE increase hippocampal LTP in-vitro, and induce a similar pattern of changes in brain electrical activity in-vivo.
While the translational clinical trials of MLE are limited by being single dose studies in a small number of subjects, they provide the first clinical evidence that the extract is well tolerated with no cardiovascular sideeffects, can induce changes in brain electrical activity, may give a faster reaction time, and decrease fatigue. These CNS activities support the reported folk-uses use of mango leaf tea as a substitute for tea and as a traditional remedy for fatigue and exhaustion. Extract Mangifera indica L., Zynamite, has nootropic potential, and larger clinical studies are needed to realise this potential.
Central nervous system activities of extract Mangifera indica L. - Laura López-Ríos, Julia C Wiebe, Tanausú Vega-Morales, Nigel Gericke - Journal of Ethnopharmacology 260 (2020)
Effects of Zynamite on cognitive function
In conclusion, a single dose of mango leaf extract (Zynamite®) with high levels of the polyphenol mangiferin, lead to broad improvements in cognitive function that were seen across assessments spanning from 30 min to 6 h post-dose. These benefits were seen most strikingly in terms of participants’ improved attention and long-term memory task performance and in their extended performance of cognitively demanding tasks, including those requiring executive function resources.
Abstract: Extracts made from the leaves of the mango food plant (Mangifera indica L., Anacardiaceae) have a long history of medicinal usage, most likely due to particularly high levels of the polyphenol mangiferin. In rodent models, oral mangiferin protects cognitive function and brain tissue from a number of challenges and modulates cerebro-electrical activity. Recent evidence has confirmed the latter effect in healthy humans following a mangiferin-rich mango leaf extract using quantitative electroencephalography (EEG). The current study therefore investigated the effects of a single dose of mango leaf extract, standardised to contain >60% mangiferin (Zynamite®), on cognitive function and mood. This study adopted a double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over design in which 70 healthy young adults (18 to 45 years) received 300 mg mango leaf extract and a matched placebo, on separate occasions, separated by at least 7 days. On each occasion, cognitive/mood assessments were undertaken pre-dose and at 30 min, 3 h and 5 h post-dose using the Computerised Mental Performance Assessment System (COMPASS) assessment battery and the Profile of Mood States (POMS). The results showed that a single dose of 300 mg mango leaf extract significantly improved performance accuracy across the tasks in the battery, with domain-specific effects seen in terms of enhanced performance on an ‘Accuracy of Attention’ factor and an ‘Episodic Memory’ factor.
Performance was also improved across all three tasks (Rapid Visual Information Processing, Serial 3s and Serial 7s subtraction tasks) that make up the Cognitive Demand Battery sub-section of the assessment. All of these cognitive benefits were seen across the post-dose assessments (30 min, 3 h, 5 h). There were no interpretable treatment related effects on mood. These results provide the first demonstration of cognition enhancement following consumption of mango leaf extract and add to previous research showing that polyphenols and polyphenol rich extracts can improve brain function.
Keywords: cognition; attention; memory; brain; polyphenols; mangiferin; mango leaf extract
Conclusion (partial) : Clearly, a strength of the current study is that it represents the first concerted investigation of the effects of mangiferin, or indeed any xanthone glycoside, on human cognitive function. Conversely, this was, by its nature, an exploratory study, and the absence of pre-defined primary outcomes, due to a lack of previous data to guide their formulation, could be considered a limitation. Certainly the absence of primary endpoints allows a greater freedom for the interpretation of the results than will be enjoyed in future research, and it is hoped that the results of the current study will be useful in terms of directing the research questions and outcomes addressed by more studies involving this compound. It should also be acknowledged that the results herein relate to a molecule, or group of molecules (xanthones) that are unlikely to be encountered in meaningful quantities in the typical diet, and therefore the results can only realistically be extrapolated to supplementation with mangiferin-rich extracts. Whilst the results tell us little about the benefits of polyphenols consumed as part of the everyday diet it might be noteworthy that the dose of 300 mg employed here contained an amount of polyphenols that is achievable through the consumption of polyphenol rich foods. In conclusion, a single dose of mango leaf extract (Zynamite®) with high levels of the polyphenol mangiferin, lead to broad improvements in cognitive function that were seen across assessments spanning from 30 min to 6 h post-dose. These benefits were seen most strikingly in terms of participants’ improved attention and long-term memory task performance and in their extended performance of cognitively demanding tasks, including those requiring executive function resources.
Acute Effects of a Polyphenol-Rich Leaf Extract of Mangifera indica L. (Zynamite) on Cognitive Function in Healthy Adults: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study Emma L. Wightman, Philippa A. Jackson, Joanne Forster, Julie Khan, Julia C. Wiebe, Nigel Gericke and David O. Kennedy - Published: 23 July 2020 - Nutrients 2020, 12, 2194
Zynamite®: similar to Caffeine, but better
In conclusion, in vivo administration of Zynamite® or caffeine displayed a similar action on the central nervous system with respect to changing the frequency pattern of brain regional field potentials and ex vivo by changing the excitability of the hippocampus of rats. A combination of both revealed over-additive or potentiating effects in both animal models pointing to a synergy between Zynamite® and caffeine. Zynamite® has potential as a CNS-activating nutraceutical that could be used to replace caffeine.
Abstract : Zynamite®, a special extract from Mangifera indica , exerted stimulatory properties on the central nervous system during a pilot study. The question arose if Zynamite® would have a similar action on the central nervous system as caffeine. Two well established animal models were used: a) quantitation of spectral power of field potentials in the freely moving rat and b) induction of long term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus slice preparation ex vivo after one week of daily administration. In the presence of 25 mg/kg of Zynamite ®, predominantly alpha2 and beta1 spectral frequencies were attenuated in all brain areas during the first hour after administration. Exactly this pattern of frequency changes had been observed in earlier studies with i.p. administration of caffeine. Discriminant analysis confirmed this similarity by projection of Zynamite® and 0.5 mg/kg caffeine into close neighborhood and showing identical colours, which points to a similar mechanism of action in this analysis. In addition, when Zynamite® was combined with very low doses of caffeine synergistic effects were observed. Since alpha2 waves are under the control of dopamine, activation of this neurotransmitter system might be responsible for the stimulating property of Zynamite®. These results are corroborated by the results from the ex vivo study using the hippocampus slice in vitro to follow changes in excitability in the presence of 0.5 mg/kg of caffeine, 25 mg/kg of Zynamite® or their combination in comparison to Placebo after daily administration for one week. Both caffeine and Zynamite® increased LTP. LTP relates to space and time dependent memory. From these studies it is evident that both caffeine and Zynamite® act in similar ways on brain electrical activity, and have potential to improve cognitive function. Bioactive compounds of Zynamite® clearly pass the blood brain barrier to act on the central nervous system. Due to the demonstrated similarity of action, Zynamite ® has potential as a CNS-activating nutraceutical that could be used to replace caffeine.
In conclusion, in vivo administration of Zynamite® or caffeine displayed a similar action on the central nervous system with respect to changing the frequency pattern of brain regional field potentials and ex vivo by changing the excitability of the hippocampus of rats. A combination of both revealed over-additive or potentiating effects in both animal models pointing to a synergy between Zynamite® and caffeine. Zynamite® has potential as a CNS-activating nutraceutical that could be used to replace caffeine.
Keywords : Zynamite®, Mangifera indica , Caffeine, Rat, Field Potential, Hippocampus Slice, Synergy
Zynamite® (Mangifera indica Leaf Extract) and Caffeine Act in a Synergistic Manner on Electrophysiological Parameters of Rat Central Nervous System - Wilfried Dimpfel, Julia Wiebe, Nigel Gericke, Leonie Schombert - Food and Nutrition Sciences, 2018, 9, 502-518
Toxicological Evaluation of Mango Leaf Extract at 60% Mangiferin
Based on the observations made in this 90-day repeateddose oral toxicity study and the lack of mortality and toxic changes in the examined parameters, the NOAEL for MLE was determined to be 2000mg/kg bw/day inmale and female Han:Wist rats, the highest dose tested.
A battery of OECD- and GLP-compliant toxicological studies was performed on mango leaf extract (Mangifera indica) containing 60% mangiferin (MLE). No evidence of genotoxicity was found in a bacterial reverse mutation test (Ames). While evidence of clastogenic activity was noted in an in vitro chromosomal aberration test, an in vivo mammalian micronucleus test showed no findings up to the limit dose (2000 mg/kg bw). A 90-day repeated dose oral toxicity study was conducted in rats using doses of 0 (vehicle control), 500, 1000, and 2000mg/kg bw/day. Based on the lack of mortality or toxic effects in the 90-day study, the NOAEL for MLE in Han:Wist male and female rats was determined to be 2000 mg/kg bw/day, the highest dose tested.
A Toxicological Evaluation of Mango Leaf Extract (Mangifera indica) Containing 60% Mangiferin - Robin A. Reddeman , Robert Glavits, John R. Endres , Amy E. Clewell , Gabor Hirka, Adel Vértesi, Erzsébet Béres, and Ilona Pasics Szakonyiné, Journal of Toxicology Volume 2019, Article ID 4763015
Mangiferin in preventing accumulation of fat tissue
It follows that the mango leaf extract and mangiferin have potential in reducing fat tissue.
Metabolic Syndrome is seen as a global epidemic, being obesity and fat accumulation in the organs responsible for chronic inflammation. Bark extract of Mangifera indica is used in the treatment of metabolic disorders. Mangiferin is identified as the bioactive compound present in the extract. The study aimed evaluate the effect of mango leaf extract and mangiferin on the weight gain, food consumption and organ weights of wistar rats. The animals were divided into 3 groups (n = 8): G1 - cafeteria diet + DMSO, G2 - cafeteria diet + mango leaf extract and G3 - cafeteria diet + mangiferin. Concomitantly with cafeteria diet, the animals received extract and mangiferin by oral gavage, using DMSO as a vehicle for 5 days. Food intake and body weight were monitored daily. The animals were euthanized and the organs heart, liver, brain and adipose tissue were collected and weighed. There was no significant difference in weight gain, but the food intake of group G2 (76.94±9.93) showed statistically lower values compared to group G1 (117.88±17.26). The weights of organs were statistically different, being: adipose tissue, G1 (0.68±0.17) was higher than G2 (0.33±0.18) and G3 (0.41±0.09). Liver, G2 (3.94±0.42) was lower than G1 (4.79±0.42) and G3 (4.62±0.38). Heart, G2 (0.78±0.12) was lower than G1 (1.16±0.09) and G3 (1.09±0.11). Brain, G1 (1.79±0.09) was higher than G2 (1.61±0.03) and G3 (1.64±0.03). It follows that the mango leaf extract and mangiferin have potential in reducing fat tissue.
Effect of mango leaf extract and mangiferin in preventing accumulation of fat tissue in rats fed with cafeteria diet, Livia Q Queiros, 36570-000, Viçosa, Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Mangiferin decreases Plasma Free Fatty Acids
Mangiferin is a possible beneficial natural compound for metabolic syndrome by improving FFA metabolism.
Abstract ; Mangiferin has been shown to have the effect of improving dyslipidemia. Plasma free fatty acids (FFA) are closely associated with blood lipid metabolism as well as many diseases including metabolic syndrome. This study is to investigate whether mangiferin has effects on FFA metabolism in hyperlipidemic rats. Wistar rats were fed a high-fat diet and administered mangiferin simultaneously for 6 weeks. Mangiferin (50, 100, 150 mg/kg BW) decreased dose-dependently FFA and triglycerides (TG) levels in plasma, and their accumulations in liver, but increased the b-hydroxybutyrate levels in both plasma and liver of hyperlipidemic rats. HepG2 cells were treated with oleic acid (OA, 0.2 mmol/L) to simulate the condition of high level of plasma FFA in vitro, and were treated with different concentrations of mangiferin simultaneously for 24 h. We found that mangiferin significantly increased FFA uptake, significantly decreased intracellular FFA and TG accumulations in HepG2 cells. Mangiferin significantly increased AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and its downstream proteins involved in fatty acid translocase (CD36) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), but significantly decreased acyl-CoA: diacylgycerol acyltransferase 2 (DGAT2) expression and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity by increasing its phosphorylation level in both in vivo and in vitro studies. Furthermore, these effects were reversed by Compound C, an AMPK inhibitor in HepG2 cells. For upstream of AMPK, mangiferin increased AMP/ATP ratio, but had no effect on LKB1 phosphorylation. In conclusion, mangiferin decreased plasma FFA levels through promoting FFA uptake and oxidation, inhibiting FFA and TG accumulations by regulating the key enzymes expression in liver through AMPK pathway. Therefore,mangiferin is a possible beneficial natural compound for metabolic syndrome by improving FFA metabolism
Mangiferin Decreases Plasma Free Fatty Acids through Promoting Its Catabolism in Liver by Activation of AMPK, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, Public Health College, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, People’s Republic of China, Mango
Anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic potentials of mangiferin
Mangiferin showed anti-diabetic as well as hypolipidemic potentials in type 2 diabetic model rats. Therefore, mangiferin possess beneficial effects in the management of type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidemia. The present study demonstrated that mangiferin could be useful in management of type 2 diabetes associated with abnormalities in lipid profiles. The study needs to be validated in human volunteers to claim for its further usage in human volunteers.
Context: Mangifera indica (Anacardiaceae) stem bark contains a rich content of mangiferin and is used traditionally in Indian Ayurvedic system to treat diabetes.
Purpose of the study: To investigate anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic effects of mangiferin in type 1 and type 2 diabetic rats models. Streptozotocin was used to induce type 1 and type 2 diabetic rats. Mangiferin (at a dose 10 and 20mg/kg) was administrated intra-peritoneally in type 1 and type 2 diabetic rats daily up to 30 days. Biochemical parameters notably fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, very low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein were estimated. In addition, in vitro alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory effects of mangiferin were performed and IC50 values were determined.
Results: Mangiferin exhibited significant (P max 0.05) anti-diabetic as well as hypolipidemic effects by lowering FBS, TC, TG, LDL, and VLDL levels; but also with elevation of HDL level in type 2 diabetic model rats. In addition, mangiferin showed appreciable alpha amylase inhibitory effect (IC50 value 74.35±1.9μg/ml) and alpha glucosidase inhibitory effect (IC50 41.88±3.9μg/ml) when compared with standard drug acarbose (IC50 83.33±1.2μg/ml).
Conclusions: Mangiferin showed anti-diabetic as well as hypolipidemic potentials in type 2 diabetic model rats. Therefore, mangiferin possess beneficial effects in the management of type 2 diabetes with hyperlipidemia.
Conclusion : The present study demonstrated that mangiferin could be useful in management of type 2 diabetes associated with abnormalities in lipid profiles. The study needs to be validated in human volunteers to claim for its further usage in human volunteers.
Keywords: Mangiferin, Anti-diabetic, Hypolipidemic, Type 2 diabetes
Studies on the anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic potentials of mangiferin (Xanthone Glucoside) in streptozotocin-induced Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic model rats on the anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic potentials of mangiferin, B Dineshkumar, Analava Mitra, M Manjunatha, International Journal of Advances in Pharmaceutical Sciences 1 (2010) 75-85
Genotoxicity and DNA protective effects of mangiferin
This study was focused to investigate the in vitro genotoxic effects of mangiferin in the Ames test, SOS Chromotest and Comet assay. In short, mangiferin did not induce cytotoxic or genotoxic effects but it protect against DNA damage.
Mangiferin is a glucosylxantone isolated from Mangifera indica L. stem bark. Several studies have shown its pharmacological properties which make it a promising candidate for putative therapeutic use. This study was focused to investigate the in vitro genotoxic effects of mangiferin in the Ames test, SOS Chromotest and Comet assay. The genotoxic effects in bone marrow erythrocytes from NMRI mice orally treated with mangiferin (2000 mg/kg) were also evaluated. Additionally, its potential antimutagenic activity against several mutagens in the Ames test and its effects on CYP1A1 activity were assessed. Mangiferin (50-5000 μg/plate) did not increased the frequency of reverse mutations in the Ames test, nor induced primary DNA damage (5-1000 μg/mL) to Escherichia coli PQ37 cells under the SOS Chromotest. It was observed neither single strand breaks nor alkali- labile sites in blood peripheral lymphocytes or hepatocytes after 1h exposition to 10-500 μg/mL of mangiferin under the Comet assay. Furthermore, micronucleus studies showed mangiferin neither induced cytotoxic activity nor increased the frequency of micronucleated/ binucleated cells in mice bone marrow. In short, mangiferin did not induce cytotoxic or genotoxic effects but it protect against DNA damage which would be associated with its antioxidant properties and its capacity to inhibit CYP enzymes. Also 'Radioprotective Effects and Mechanism of Mangiferin and Its Derivatives on Cells and Zebrafiish'
Evaluation of genotoxicity and DNA protective effects of mangiferin, a glucosylxanthone isolated from Mangifera indica L. stem bark extract, Departamento de Farmacología, Centro de Bioproductos Marinos (CEBIMAR), Rodeiro I, Hernandez S, Morffi J, Herrera JA, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Delgado R, Espinosa-Aguirre JJ.
Phytochemical and pharmacological investigations on mangiferin
Mangiferin has prominent pharmacological actions corroborated by numerous research studies. Potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, antioxidant, immunomodulator, antitumor, antiviral, anthelmintic, antiallergic, antihistaminic, cardioprotective, anticholinergic, antiamoebic and antidiabetic effects have been found to be exerted by mangiferin . Though, considerable research has been and are being done on mangiferin and its plant source. Yet, the potential therapeutic effects of mangiferin have not been fully exploited till now. There is an ample scope for researchers to work further in this area.
Mangiferin, a C- glucopyranoside of 1, 3, 6, 7- tetrahydroxyxanthone, has been isolated from various parts of Mangifera indica (Anacardiaceae). The conclusive structure of mangiferin has been established by various researchers using a wide range of chemical and spectral analytical techniques. Mangiferin has been traditionally used in some parts of world as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, antioxidant, immunomodulator, anti- tumor, antiviral, and anthelminthic and in obesity treatment. The present article is an attempt to encompass various aspects and details related to the characterization of mangiferin and its subsequent pharmacological screening. The literature data on mangiferin has been comprehensively reviewed and evaluated by the authors and hence, the article contains brief description of phytochemical and pharmacological investigations conducted on mangiferin till now and thus may prove as a guiding force for further research in this particular area
Key words: Mangifera indica, mangiferin
M. indica: traditional use M. indica is commonly used in folk medicine for a wide variety of remedies. The root, bark, leaves, flowers, unripe and ripe fruit are acrid, cooling and astringent to the bowels and have been employed to cure “vata”, “pitta”, and “kapha” (Ayurvedic terminology). The parts of M. indica mentioned above have also been employed traditionally for treatment of leucorrhoea, bad blood; dysentery, piles, bronchitis, biliousness, urinary discharges, throat troubles, vaginal troubles, hiccough, ophthalmia, eruption, asthma and labouring under habitual constipation. It is also used as aphrodisiac, tonic, appetizer, beautifier of complexion, hiccough, laxative, diuretic, stomachic, antisyphilitic and for tanning purposes in various parts of the world.
The authors are of the opinion that there exists a good correlation between traditional and folklore use of mangiferin and the results of the recent research studies on the same.
Phytochemical and pharmacological investigations on mangiferin, Shashi Kant Singh, India
Mangiferin on hyperglycemia and atherogenicity
The present study demonstrates that mangiferin possesses significant antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antiatherogenic properties thus suggesting its beneficial effect in the treatment of diabetes mellitus associated with hyperlipidemia and related cardiovascular complications
In the present study, the effect of mangiferin (a xanthone glucoside, isolated from the leaves of Mangifera indica) on the atherogenic potential of streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetes was investigated. In addition, the effect of mangiferin on oral glucose tolerance in glucose-loaded normal rats was also determined. The chronic intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of mangiferin (10 and 20 mg/kg) once daily (o.d.) for 28 days exhibited antidiabetic activity by significantly lowering fasting plasma glucose level at different time intervals in STZ-diabetic rats. Further, mangiferin (10 and 20 mg/kg, i.p.) showed significant antihyperlipidemic and antiatherogenic activities as evidenced by significant decrease in plasma total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels coupled together with elevation of high- density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) level and diminution of atherogenic index in diabetic rats. In addition, the chronic administration of mangiferin (10 and 20 mg/kg, i.p.) for 14 days significantly as well as markedly improved oral glucose tolerance in glucose-loaded normal rats suggesting its potent antihyperglycemic activity. The accumulating evidences suggest that both pancreatic and extrapancreatic mechanisms might be involved in its antidiabetic or antihyperglycemic action.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that mangiferin possesses significant antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antiatherogenic properties thus suggesting its beneficial effect in the treatment of diabetes mellitus associated with hyperlipidemia and related cardiovascular complications
Keywords: Mangiferin; Streptozotocin; Atherogenic; Diabetic
Effect of mangiferin on hyperglycemia and atherogenicity in streptozotocin diabetic rats - S. Muruganandan, K. Srinivasan, S. Gupta, P.K. Gupta, J. Lala, Journal of Ethno Pharmacology, 97 (2005) 497-501
Antidiabetic activity on extracts of Mangifera indica
The aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of Mangifera indica significantly reduced the high fasting glucose levels in Alloxan monohydrate -induced diabetic rats. This suggests that the extracts may possess insulin like effect on peripheral tissues by either promoting glucose uptake or metabolism, by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis (1) or absorption of glucose into the muscles and adipose tissues (16), by the stimulation of a regeneration process and revitalization of the remaining beta cells (22). Thus the aqueous leaf extracts of Mangifera indica anti-diabetic properties.
After induction of diabetes, leaf extract of Mangifera indica has been given to the treated rats to establish the protective role. Different doses of Mangifera indica were evaluated for hypoglycemic activity in normal and Alloxan diabetic rats. The oral administration of aqueous, ethanol, hexane extracts at a dosage of 0.35g/kg and 0.7 g/kg body weight exhibited a significant antidiabetic activity in Alloxan monohydrate diabetic rats, whereas in normal rats no hypoglycemic activity was observed.
Discussion: The aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of Mangifera indica significantly reduced the high fasting glucose levels in Alloxan monohydrate -induced diabetic rats. This suggests that the extracts may possess insulin like effect on peripheral tissues by either promoting glucose uptake or metabolism, by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis (1) or absorption of glucose into the muscles and adipose tissues (16), by the stimulation of a regeneration process and revitalization of the remaining beta cells (22). Thus the aqueous leaf extracts of Mangifera indica anti-diabetic properties.
Keywords: Anti hyperglycemia; Mangifera indica, Alloxan monohydrate, diabetic rats.
Antidiabetic activity on extracts of Mangifera indica in Alloxan monohydrate induced diabetic rats, D Peer Basha, Katikala Prasanth Kumar, Bulusu Bhanu Teja, Mannam Subbarao, Drug Invention Today, ISSN: 0975-7619
Therapeutic and cosmetic applications of mango mangiferin
Mangiferin is used in cosmetics mainly due to its antioxidant and UV-protecting properties. The UV-protecting property is based on the evidence that mangiferin and its isomers increased the expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs), and inhibited the expression of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) improving cell response to heat stress.
Introduction :Mangiferin, a natural C-glucoside xanthone [2-C-b-D- glucopyranosyl- 1, 3, 6, 7-tetrahydroxyxanthone], is abundantly present in young leaves and stem bark of the mango tree. The xanthonoid structure of mangiferin with C-glycosyl linkage and polyhydroxy components contributes to its free radical-scavenging ability, leading to a potent antioxidant effect as well as multiple biological activities.
Areas covered : An extensive search was carried out to collect patent information on mangiferin and its derivatives using various patent databases spanning all priority years to date. The patents claiming therapeutic and cosmetic applications of mangiferin and its derivatives were analyzed in detail. The technology areas covered in this article include metabolic disorders, cosmeceuticals, multiple uses of the same compound, miscellaneous uses, infectious diseases, inflammation, cancer and autoimmune disorders, and neurological disorders.
Expert opinion : Mangiferin has the potential to modulate multiple molecular targets including nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) signaling and cyclooxygenase- 2 (COX-2) protein expression. Mangiferin exhibits antioxidant, antidiabetic, antihyperuricemic, antiviral, anticancer and antiinflammatory activities. The molecular structure of mangiferin fulfils the four Lipinski’s requisites reported to favor high bioavailability by oral administration. There is no evidence of adverse side effects of mangiferin so far. Mangiferin could thus be a promising candidate for development of a multipotent drug.
Discussion (partial) : Mangiferin is used in cosmetics mainly due to its antioxidant and UV-protecting properties. The UV-protecting property is based on the evidence that mangiferin and its isomers increased the expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs), and inhibited the expression of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) improving cell response to heat stress. These targets could be used to evaluate the UV and heat-protecting properties of the recently developed mangiferin derivatives. The information provided in this review highlights that mangiferin and its derivatives can be regarded as a source of new drugs and cosmetics. Cheminformatics tools can be used to carry out further studies on the relationship of structure and activity amongst mangiferin and its derivatives. The results can be utilized to develop pharmacophores against the possible targets which in turn can be utilized as a basis to design new derivatives with drug-like properties. Experimental evidence as well as predictive computational studies done so far raise a possibility that mangiferin could be developed in to a multitarget drug.
Keywords : anticancer, antiinfectious, antiinflammatory, antioxidant, cosmeceutical, mangiferin,mangiferin derivative, metabolic disorder
Therapeutic and cosmetic applications of mango mangiferin: a patent review, Expert Opin. Ther. Patents (2013) 23 (12): 1561-1580, Manasi Telang, Sivakami Dhulap
Mango ameliorate Plasma Ethanol level
This study suggests that mango flesh and peel could be used as resources for functional foods intended to decrease plasma ethanol level after ethanol uptake.
The ameliorating effects of Mango ( ) flesh and peel samples on plasma ethanol level were investigated using a mouse model. Mango fruit samples remarkably decreased mouse plasma ethanol levels and increased the activities of alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase. The 1H NMR based metabolomic technique was employed to investigate the differences in metabolic profiles of mango fruits, and mouse plasma samples fed with mango fruit samples. The partial least squares discriminate analysis of 1H NMR spectral data of mouse plasma demonstrated that there were clear separations among plasma samples from mice fed with buffer, mango flesh and peel.
A loading plot demonstrated that metabolites from mango fruit, such as fructose and aspartate, might stimulate alcohol degradation enzymes. This study suggests that mango flesh and peel could be used as resources for functional foods intended to decrease plasma ethanol level after ethanol uptake.
Keywords: 1H-NMR; Mangifera indica; mango; metabolomics; plasma ethanol level.
Ameliorating effects of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit on plasma ethanol level in a mouse model assessed with 1H NMR based metabolic profiling - So Hyun Kim, Somi K. Cho, Tae Sun Min, Yujin Kim, Seung Ok Yang, Hee Su Kim, Sun Hee Hyun, Hana Kim, Young Suk Kim and Hyung Kyoon Choi - doi: 10.3164/ jcbn.10 96 - J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. vol. 48
Whitepaper and studies reports for Zynamite [as beg. of 2020]
Zynamite® gives sustained focus and increases mental and physical energy without any negative side effects like jitters, nausea, anxiety or increased blood pressure.
Zynamite® crosses the blood brain barrier and has a strikingly similar brain activity activation on EEG to caffeine.
Nektium’s sports performance studies demonstrate that Zynamite® has better ergogenic activity than caffeine, without cardiovascular or other side effects. Zynamite® is doping-free, tested against WADA list of doping agents.
The results of these clinical studies demonstrate that Zynamite® enhances attention, reduces mental fatigue and improves reaction time - results typically shown for caffeine. The advantage of Zynamite® is that this extract also reduced stress, and there were no side-effects, including no changes in heart rate or blood pressure
What Do Tired People Need ? Stressed or fatigued people lack enthusiasm and mostly feel exhausted and desperate. What they desire is a sustained boost of energy that improves physical performance, concentration, attention, alertness and mood.
The Problem With Caffeine Because of the mental energy and focus provided by caffeine, billions of cups of coffee are consumed daily to assist people to cope. However, caffeine is addictive and most people consume too much of it and suffer from its side effects and withdrawal symptoms.
Ideal For Sports Performers Zynamite® is doping free and ideal for sports professionals or weekend warriors who are aiming to increase their physical and mental energy performance.
Preclinical Studies On Zynamite : Results demonstrated that the pattern of electrical activation for both Zynamite® and caffeine are remarkably similar in the brain frontal cortex and in the hippocampus
CONCLUSION : Zynamite® crosses the blood brain barrier and has a strikingly similar brain activity activation on EEG to caffeine. 1/Zynamite® combined with caffeine has a synergistic effect, 2/Zynamite® and caffeine have two have different molecular mechanisms of action, 3/Zynamite® is a COMT inhibitor. COMT modulates the levels of dopamine, serotonin and nor-epinephrine.
Long-Term Potentiation
In a study comparing the effect of Zynamite®, caffeine and the combination of Zynamite® + caffeine on LTP, Zynamite® had a greater effect on LTP than caffeine, while the combination of Zynamite® + caffeine demonstrated a remarkable synergy in increasing LTP
CONCLUSION Zynamite® increased Long-Term Potentiation more than caffeine. - Zynamite® can increase attention, learning and memory and can thus be considered as a nootropic that can be used to completely replace caffeine or dramatically reduce the dose of caffeine in a product.
Clinical Studies On Sports Performance
Both Zynamite® formulations enhanced exercise sprint performance, likely by improving brain oxygenation and allowing a higher muscle extraction of oxygen. These effects were observed following 48h and 15 days of supplementation without significant differences between the two doses tested7
Mean Power Output (MPO) : Compared to placebo, MPO was improved in athletes taking Zynamite® + Luteolin in the 30s Wingate test by 5% (p=0.009), while in the Wingate test following IR, the improvement was 15% (p=0.04). Compared to placebo, MPO was improved in athletes taking Zynamite® formulations in the prolonged 60s sprint by 6% (p=0.007) for Zynamite® + Luteolin and 7% (p=0.008) for Zynamite® + Quercetin.
Peak Power Output (PPO) : Compared to placebo, PPO was improved in athletes taking Zynamite® formulations in sprints performed at high exhaustion following IR, by 10.3% for Zynamite® + Luteolin and 19.4% for Zynamite® + Quercetin
Oxygen Uptake (vo2max) And brain Oxygenation : Zynamite® + Quercetin improved VO2max by 6.1%, with a corresponding increase in brain oxygenation of 11% in women.
Muscle Oxygenation : After the ingestion of 140mg of Zynamite® + Luteolin, the quadriceps muscle tissue oxygenation index (TOI) during sprint exercise was 3% lower (p= 0.007) after 48h and 5% lower (p= 0.09) after 15 days, indicating enhanced muscle O2 extraction.
Pain Perception : Pain perception was reduced in Zynamite® in formulations compared to placebo (p= 0.068).
CONCLUSION : Nektium’s sports performance studies demonstrate that Zynamite® has better ergogenic activity than caffeine, without cardiovascular or other side effects. Zynamite® is doping-free, tested against WADA list of doping agents.
Clinical Studies On Mental Energy : Nootropics boost cognitive function and memory and improve reaction time, focus and performance with no negative rebound effects, like those experienced from caffeine. Popularity for nootropics has increased significantly in recent years. The nootropic effect of 500mg Zynamite® was studied in two randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled cross-over pilot clinical trials. 16 participants took Zynamite® compared to placebo.
Mood And Stress : The study showed that Zynamite® significantly reduced fatigue after only 1.5 hours, analyzed with the Profile of Mood States questionnaire (POMS). Zynamite® reduced stress during the Calculation Performance Tests, evidenced by Galvanic skin response.
Heart Rate Variability And Blood Pressure : Zynamite® had no side effects and no change in heart-rate variability or blood pressure over the course of the study - variables typically affected by caffeinated products.
EEG : During performance of two cognitively demanding challenges, a Number Sequence Test (NST) and a Number Connection Test (NCT), Zynamite® had a significant activating effect on the brain compared to placebo as determined by frequency analysis of the changes in electrical activity across six brain wave frequency ranges (colour coded) in the EEG of the association cortex (change from time-averaged baseline assigned as 100% p max 0.05, p max 0.001.
Psychometric Tests : Reaction time was significantly faster for Zynamite® compared to placebo.
CONCLUSION : The results of these clinical studies demonstrate that Zynamite® enhances attention, reduces mental fatigue and improves reaction time - results typically shown for caffeine. The advantage of Zynamite® is that this extract also reduced stress, and there were no side-effects, including no changes in heart rate or blood pressure
Toxicology : To confirm the safety of ingestion of Zynamite®, Nektium commissioned a 90-day in vivo repeat dose oral gavage toxicity study of Zynamite®. Based on the observations made the No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) was determined as follows. NOAEL: 2000 mg/kg bw/day.
Nektium : committed to a sustainable future
Our partner Nektium has just published its sustainability report, highlighting its initiatives and commitments in terms of environmental and social responsibility.
Zynamite® - a natural exercise-mimetic ingredient
A recent study has confirmed an unprecedented scientific finding, which further supports the benefits of Zynamite® in the development of sports activity and its potential to enhance muscle performance.
Newsletter Sept. 2021 - Française
Une sélection rapide des toutes dernières informations sur nos études et nos extraits de plantes standardisés et objectivés, pour la nutrition et la cosmétique.
New ESSNA awards for Nektium
The European Specialist Sports Nutrition Association [ESSNA] honored Nektium in three categories: Zynamite®: Best “free from” product Zynamite®: Highly commended "2019 Game changer" Rhodiolife®: Best Targeted Sports Nutrition Product 50+
Nootropic effect of Zynamite® in publication
In the first study MLE improved all scores for Profile of Mood States (POMS), with the score for “fatigue” significantly improved.
New study at a single dose Zynamite®
Zynamite® clinical trial demonstrates sustained effect on brain functions from a single dose. One dose of Zynamite® is enough to significantly improve performance in a range of cognitive tasks including enhanced attention and memory, reports new clinical data.
Zynamite and Sport - new study
New clinical study published about Zynamite® : "A Single Dose of The Mango Leaf Extract Zynamite® in Combination with Quercetin Enhances Peak Power Output During Repeated Sprint Exercise in Men and Women"
NutraIngredients Awards 2018 for Zynamite®
Zynamite® - our patent-pending proprietary mango leaf extract ideal for boosting mental and physical energy - won the NutraIngredients Awards 2018 during Vitafoods, Geneva.
Are you interested in our solutions and want to know more?
Becarre Natural represents, distributes and develops natural actives extracts from plants for nutrition health and cosmeceutical.
Contact us