Rhodiola 5%

Download the document
Rhodiola 5%
Rhodiolife® - The benchmark brand: Stress, memory, attention, energy, immunity,... adaptogen
Rhodiolife generates sustained energy and promotes wellness including psychological, emotional and physical conditioning. Rhodiolife brings you safety and quality..Rhodiolife® is a powerful adaptogen that produces a non-specific state of adaptation and resistance in the body to physical, emotional and environmental stress. Rhodiolife® is experiential, a distinct advantage over other adaptogens. Even a single dose provides tangible activation of mental energy and improved focus..Nektium historically extracted from very high quality Rhodiola, under close partnership, the result of many years of collaboration with local operators in order to guarantee sustainability and maximum traceability. As one of the world's leading producers, Nektium is sourcing the roots directly from the Altai mountains, respecting a socially responsible controlled harvest, according to the "Who Guidelines on Good Agricultural Practice". They will regularly inspect the crops. This allowed them to have access to the roots, even during shortage, working also against speculation..In addition to the systematic control of all batches by barcode DNA, PCR sequence, UHPLC fingerprint, Nektium checks the complete HPLC confirming the conformity of the extract with the original plant, with a constant quality: indeed, the markers do not are not the only assets in the profile. Nektium has put in place a composition guarantee by continuously comparing the extract and the plant. Rhodiolife® has been registered with SIDI with Success (joint US program for product registration).- Comes from Altai mountains , preserved area – control of PAH (although Rhodiola extracts are sensitive to PAH, our Rhodiolife is always below the 10ppb, thanks to its unique and protected location.)
- Only the three Rosavins are controlled in our Rhodiolife : It exists on the market many 3% or 5% of 'total rosavins' but including 4 or 5 molecules instead of the 3 (Rosavin, Rosine, Rosarin but also rosiridin or even sometimes tyrosol)
- Dried at low temperature to retain the bioactivity
- Processed in GMP approved unit, "doping free" by BSCG
- Only RhodioLife’s unique “fingerprint” composition consistently provides the spectrum of nutrients found in the root of the plant which are responsible for its biological activity.
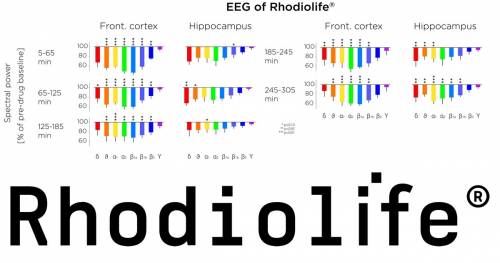
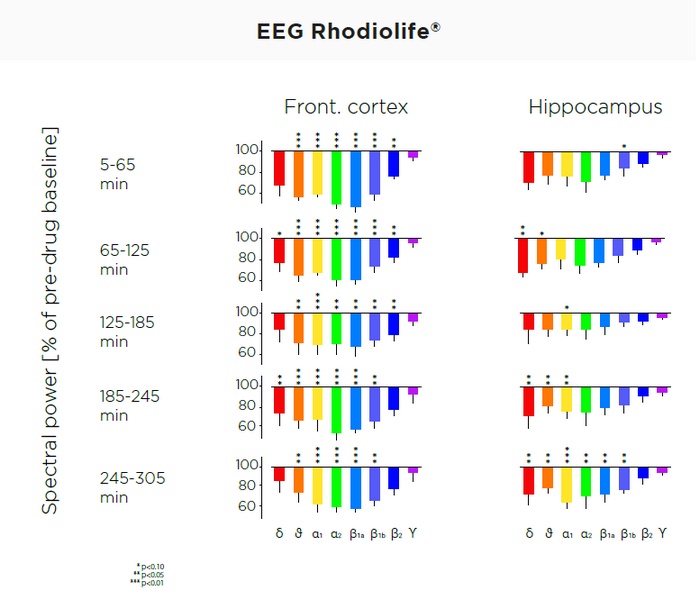
- Mental energy - Analysis of the signature of EEG to measure brain activity, action on the central nervous system, stress and depression. It was shown to be very similar to the signatures for caffeine, Guarana (Paullinia cupana) and Ginkgo biloba2
- Memory : Rhodiolife® increases Long-Term Potentiation (LTP), an effect related to improvements in spatial and temporal memory that enables the brain to form memories and helps athletes to automate coordination skills
- Mood : a pilot study of a product containing Nektium´s Rhodiolife® had significantly reduced Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS). Other studies suggest a possible antidepressant action of Rhodiola rosea extract.
- Neuroprotection : The effect of Rhodiolife® on genes related to neurodegeneration and neuroprotection was tested : significant upregulation (p<0.05) of 3 GPCR-genes
- Sport, ATP, HSP70 : Rhodiolife® protects muscle cells against oxidative stress, improves physical work capacity, assists recovery and protects the muscle tissue. It increased time to exhaustion (p<0.05) and VO2max (p<0.05). Comparison of Rhodiolife® Rhodiola rosea and Rhodiola crenulata showed that Rhodiolife® is more effective at improving physical work capacity through ATP. Rhodiolife® modifies the production of HSP70 in muscle cells under conditions of increased oxidative stress, such as that caused by intense physical exercise and protects muscles from stress related damage
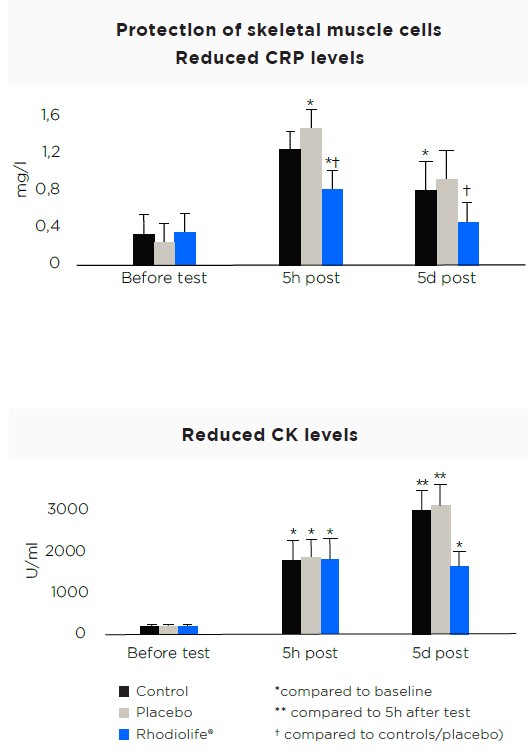
- Anti-inflammatory: The results demonstrated that it decreases inflammation and reduces COX-2. CRP (C-reactive protein) increases were smaller than in the control and placebo groups and had returned to normal levels much faster after exercise. The CK ((creativine kinase) activity in the Rhodiolife®-treated group was significantly lower than in the placebo and control groups
- Efficacy and safety, including genotoxicity performed on Rhdoilife itself
- Immune defenses (test on subject serum during a marathon and post-race) : Rhodiolife® protects against virus replication (p= 0.03).
Rhodiola extract standardized to 5% Rosavins and min 1.8% salidroside: spray dried. This grade corresponds to the native and is soluble in water. 100% Rhodiola
Recommended doses according to the studies: Rhodiolife® 5%: 100-250mg twice a day
Rhodiola roea - The adaptogen with rapid and lasting effects for physical activity and performance
Rhodiola rosea (golden root, rose root, roseroot, Aaron's rod, Arctic root, king's crown, lignum rhodium, orpin rose) - not to be confused with Rhodiola crenulata which seems similar in specifications but without providing beneficial properties - is a plant to perennial flowers of the Crassulaceae family, growing in cold and wild regions of northern and mountainous Europe - it has been used for centuries to cope with the cold Siberian climate and stressful life: feeling better every day . Collection is regulated, and only roots of a certain age should be harvested for best efficiency (specific profile in three rosavins, salidroside - a powerful antioxidant in synergy with rosavins - and tannins..In addition to its adaptogenic properties, it promotes physical activity and performance, and reduces stress, from the first dose (faster and longer-lasting action than other adaptogens).- It is involved in the regulation of adrenaline and the production of cortisol (resistance).
- It supports the activity of the adrenal glands
- It promotes brain function by neuronal stimulation (neurotransmitter: dopamine, serotonin, noradrenaline)
- It acts on the regulation of heart rate and blood pressure
- It is involved in the biological reactions necessary for good immune, pulmonary, cardio and endocrine health.

An extensive scientific literature has validated many of the traditional Siberian uses of Rhodiola rosea roots for adaptogenic, mental energy and endurance-enhancing effects.
Rhodiolife® is a highly versatile, experiential adaptogen that can be used in mental energy, mood, nootropic and sports performance products.
Nektium and partners have built on this impressive research base with preclinical and clinical studies on Rhodiolife® that have demonstrated rapid onset of brain-activating activity, increased Long-Term Potentiation, anxiolytic and antidepressant potential, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activity, enhanced physical work capacity and recovery, and skeletal muscle protective activity.
Rhodiola rosea can impact anxiety, stress, cognition and other mood symptoms
 |
Rhodiolife® increases LTP (Long-Term Potentiation), an effect related to improvements in spatial and temporal memory that enables the brain to form memories and helps athletes to automate coordination skills.
While many studies on various extracts and formulations of Rhodiola rosea have demonstrated benefits in diverse models of physical and psychological stress, Nektium pioneered the investigation of the Central Nervous System (CNS) activities of Rhodiolife® using cuttingedge neurophysiological studies including in vivo functional electroencephalogram (EEG). In a study, a single dose of Rhodiolife® was demonstrated to result in a very rapid onset of brain activation on EEG, an effect that had a long duration of action, lasting at least five hours. NeuroprotectionReports have indicated neuroprotective potential for Rhodiola rosea, and effect of Rhodiolife® on genes related to neurodegeneration and neuroprotectiont. MoodA daily dose of 340mg for 10 weeks, had significantly reduced Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS) scores. |
Anti-inflammatory, Sport and muscle health
Rhodiolife® protects muscle cells against oxidative stress10, improves physical work capacity, assists recovery and protects the muscle tissue of healthy untrained volunteers during exerciseImproved endurance exercise performanceRhodiola rosea can improve endurance exercise capacity in healthy young volunteers, and endurance exercise performance by decreasing the perception of effort.Improved physical working capacity and recoveryRhodiola rosea is more effective than Rhodiola crenulata at improving physical work capacity (effect on ATP, probably due to rosavins, only present in Rhodiola rosea).Immune supportIn the presence of serum from Rhodiolife® and placebo supplemented subjects, Rhodiolife® protects against virus replicationHeat Shock Protein (HSP70) improves muscle protection and recoveryCell cultures without Rhodiolife® pre-treatment showed a 25% decrease in cell viability following exposure to H2O2, while no significant decrease in cell viability was detected in cells pre-treated with Rhodiolife®. Rhodiolife® increases expression of HSP70 genes. After exhausting physical exercise on a cycle ergometer. In the group treated with Rhodiolife®, CRP (C-reactive protein) increases were smaller. 5 days after exercise, the CK activity in the Rhodiolife®-treated group was significantly lower than in the placebo and control groups. Thus, treatment of untrained volunteers with Rhodiolife® reduced inflammation, evidenced by decreased CRP, CK and reduced muscle damage. |
 |
-
Studies & Documents(36)
-
News(6)
Antiviral activity of Rhodiola rosea
These results indicate that bioactive compounds in the serum of subjects ingesting Rhodiola rosea may exert protective effects against virus replication following intense and prolonged exercise by inducing antiviral activity.
Abstract : Rhodiola rosea, a medicinal plant with demonstrated adaptogenic properties, has recently been reported to contain active compounds with antimicrobial activity. The goal of this study was to measure the antiviral and antibacterial properties of the bioactive metabolites of Rhodiola rosea in the serum of experienced marathon runners following supplementation. Marathon runners, randomly divided into two groups, ingested 600 mg/day of Rhodiola rosea (n=24, 6 female, 18 male) or placebo (n=24, 7 females, 17 males) for 30 days prior to, the day of, and 7 days post-marathon. Blood serum samples were collected the day before, 15 min post-, and 1.5 h post-marathon. Serum from Rhodiola rosea-supplemented runners collected after marathon running did not attenuate the marathon-induced susceptibility of HeLa cells to killing by vesicular stomatitis virus.
However, the use of Rhodiola rosea induced antiviral activity at early times post-infection by delaying an exercise-dependent increase in virus replication (P=0.013 compared to placebo). Serum from both groups collected 15 min post-marathon significantly promoted the growth of Escherichia coli in culture as compared to serum collected the day before the marathon (P=0.003, all subjects). Furthermore, the serum from subjects ingesting Rhodiola rosea did not display antibacterial properties at any time point as indicated by a lack of group differences immediately (P=0.785) or 1.5 h (P=0.633) post-marathon.
These results indicate that bioactive compounds in the serum of subjects ingesting Rhodiola rosea may exert protective effects against virus replication following intense and prolonged exercise by inducing antiviral activity.
Keywords: Rhodiola rosea, physical activity, vesicular stomatitis virus, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, bacterial growth
Rhodiola rosea exerts antiviral activity in athletes following a competitive marathon race - Maryam Ahmed, Dru A. Henson, Matthew C. Sanderson, David C. Nieman, Jose M. Zubeldia and R. Andrew Shanely, ORIGINAL RESEARCH published: 31 July 2015 doi: 10.3389/ fnut . 2015 . 00024
Rhodiola protects muscle cells against oxidative stress
Rhodiola (Nektium) modulates the expression of Heat Shock. Rhodiola Rosea is a perennial plant in the Crassulaceae family growing in cold regions that has been traditionally used as a potent adaptogen. More recently, it has been postulated that adaptogens may exert their functions partially by modulating the expression of molecular protection factors such as heat shock proteins (HSP). The aim of our study was to assess whether our proprietary Rhodiola Rosea extract (RhodioLife®) was able to modulate HSP70 expression in skeletal cells when exposed to peroxide-induced oxidative stress.
Rhodiola rosea is a perennial plant in the Crassulaceae family, recently postulated to exert its adaptogenic functions partially by modulating the expression of molecular factors such as heat shock proteins (HSP). The aim of this study was to analyze the efficacy of a Rhodiola rosea extract (Rhodiolife) in protecting murine skeletal muscle cells (C2C12 myotubes) from chemically induced oxidative stress and to establish whether modulation of HSP70 expression is observed. C2C12 cells treated with Rhodiolife did not experience any loss of viability (p min 0.05) at concentrations of 1–100 μg/mL for up to 24 h. In control cultures, viability decreased 25% following exposure to 2mM H2O2 (1 h). However, no significant decrease in viability in cells pre-treated with extract at concentrations as low as 1 μg/mL was observed. HSP70 mRNA levels were up-regulated two-fold in cell cultures treated with Rhodiolife (10 μg/mL), and expression was further enhanced by exposure to H2O2 (six-fold, p max 0.05). HSP70 protein levels were maintained in pre-treated cell cultures compared to controls but was significantly lower ( 50%) in cells lacking treatment exposed to H2O2. The present results indicate that Rhodiolife protects C2C12 myotubes against peroxide-induced oxidative stress through the modulation of the molecular chaperone HSP70.
Discussion (partial) : Based on our results, we propose that Rhodiolife may exert protective effects against oxidative damage through modulation of HSP70. In myotube cell cultures, Rhodiolife activated this protective mechanism resulting in preservation of cell viability and increase in survival rate in vitro.
Keywords: adaptogen; Rhodiola rosea; muscle; oxidative stress; HSP70.
A Rhodiola Rosea Root Extract Protects Skeletal Muscle Cells Against Chemically Induced Oxidative Stress by Modulating Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Expression, Phytother. Res. 28: 623–628 (2014), Aaron Hernández-Santana, Verónica Pérez-López, Jose María Zubeldia and Miguel Jiménez-del-Rio
Rhodiola rosea for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
R. rosea appears to reduce symptoms of anxiety in individuals suffering from GAD. Given this, a favorable side-effect profile, and the popularity of herbal remedies in our culture, R. rosea is deserving of further study in GAD and other stress-related conditions.
Background: Rhodiola rosea is an herbal supplement that many in the general population in Russia and elsewhere in the world have used for decades to alleviate everyday anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Whether R. rosea is effective in reducing similar symptoms in clinical samples is unknown. The goal of this pilot study was to evaluate whether R. rosea is effective in reducing symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Method: Ten (10) participants with a DSM-IV diagnosis of GAD, recruited from the UCLA Anxiety Disorders Program and between the ages of 34 and 55, were enrolled in this study from November 2005 to May 2006. Participants received a total daily dose of 340 mg of R. rosea extract for 10 weeks. Assessments included the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HARS), the Four-Dimensional Anxiety and Depression Scale, and the Clinical Global Impressions of Severity/Improvement Scale. Results: Individuals treated with R. rosea showed significant decreases in mean HARS scores at endpoint (t = 3.27, p = 0.01). Adverse events were generally mild or moderate in severity, the most common being dizziness and dry mouth. Conclusions: Significant improvement in GAD symptoms was found with R. rosea, with a reduction in HARS scores similar to that found in clinical trials. These preliminary findings warrant further exploration of treatment with R. rosea in clinical samples.
A Pilot Study of Rhodiola rosea (Rhodax® = Rhodiola from Nektium) for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Alexander Bystritsky, Lauren Kerwin, and Jamie D. Feusner, The Journal Of Alternative And Complementary Medicine Volume 14, Number 2, 2008, pp. 175–180
Rhodiola stimulates hippocampus, model for memory
Rosavin, salidroside and various R. rosea extracts potentiated the in vitro electric stimulation of an intrahippocampal electric circuit, which resulted in higher responses of pyramidal cells in isolated hippocampus slices.
Rhodiola rosea L. roots and rhizome extracts are active ingredients in adaptogenic herbal medicinal products (HMP) and dietary supplements for temporary relief of symptoms of stress, such as fatigue and weakness. R. rosea extract has a stimulating effect on the CNS, suggesting potential benefits on cognitive functions, memory, learning, and attention. The reproducible efficacy and quality of preparations of the underground parts of R. rosea depend on the highly variable content of the active markers, salidroside and rosavin, which affect the quality of HMP and dietary supplements. However, it is not clear which analytical markers are important for assessing the efficacy of R. rosea preparations intended for use in aging-induced mild cognitive disorders, such as attenuated memory, attention, and learning. Furthermore, the activity of various commercial R. rosea extracts has not been correlated with their content. Here, the biological activities of salidroside, rosavin, and seven commercial extracts of underground parts of R. rosea were assessed using a synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation (LTP) of synaptic transmission in hippocampus slices. A high degree of variation in the content of all active markers was observed. One extract from China lacked rosavin, and there was even variation in the extracts from the Altai geographic region. In vitro, rosavin, salidroside and all tested R. rosea extracts potentiated electric stimulation of an intra-hippocampal electric circuit, which resulted in higher responses of the pyramidal cells in isolated hippocampus slices. Rosavin was more active at higher concentrations than salidroside; while, salidroside was more effective at lower concentrations. The highest content of both active markers was found in the extracts that were active at the lowest concentrations tested; while, some extracts contained some other compounds that presumably reduced the efficacy due to antagonistic interactions. Standardized content of active markers is necessary for the quality control of herbal preparations containing R. rosea extracts, but insufficient for assessment of their potential efficacy. Additional bioassays are needed to assure the reproducible pharmacological activity of R. rosea extracts; therefore, the LTP of synaptic transmission in hippocampus slices may serve as a validation tool for the quality control of R. rosea extracts.
In conclusion, rosavin, salidroside and various R. rosea extracts potentiated the in vitro electric stimulation of an intrahippocampal electric circuit, which resulted in higher responses of pyramidal cells in isolated hippocampus slices. Rosavin was more active in higher concentrations than salidroside; while, salidroside was more effective at lower concentrations. The highest content of both active markers was found in the extracts that were active at the lowest concentrations. Although, this correlation was not applicable to some extracts containing other compounds that presumably reduced the efficacy due to antagonistic interactions. The standardized content of active markers is necessary for the quality control of herbal preparations containing Rhodiola extracts, but insufficient for assessment of their potential efficacy. The application of bioassays should be required for adequate assessment of the quality and efficacy of R. rosea extracts.
Keywords: Rhodiola rosea, salidroside, rosavin, long-term potentiation, hippocampus, quality control, UPLC
Assessing the Quality and Potential Efficacy of Commercial Extracts of Rhodiola rosea L. by Analyzing the Salidroside and Rosavin Content and the Electrophysiological Activity in Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation, a Synaptic Model of Memory, Wilfried Dimpfel, Leonie Schombert and Alexander G. Panossian, Frontiers in Pharmacology, May 2018, Volume 9, Article 425
Central nervous system / cognitive and Rhodiola rosea
The combined information predicts stimulant and cognitive function-enhancing activities in humans for the Rhodiola extract, which could also be used as a possible caffeine-replacement, and antidepressant and analgesic activity for the Oenothera extract.
The combination of Tele-Stereo-EEG in vivo and hippocampal slice preparation in vitro may be sufficient as a screening tool in order to gather enough pharmacological information to predict a clinical indication for herbal preparations anticipated to have CNS activity, especially when compared to a database of electropharmacograms for reference CNS-active pharmaceuticals.
Abstract : To find possible therapeutic applications involving the Central Nervous System (CNS) for herbals is a major challenge during functional food and drug discovery and development programmes.
Despite the availability of numerous in vitro and in vivo tests, there is no single agreed screening procedure for pharmacological testing of herbal extracts with anticipated CNS activity. Experience gained from more than 25 years of testing has shown that two models give reasonably reliable orientation for future CNS applications: construction of an electropharmacogram based on wireless recording of field potentials from the depth of the brain of freely moving rats (Tele-StereoEEG) and recording of the population spike produced by pyramidal cells from hippocampal slices in vitro. A combination of these two methods has now been used to characterize the pharmacological profile of extracts from Rhodiola rosea root, Oenothera paradoxa seeds and Paullinia cupana seeds. Spectral analysis of field potentials revealed attenuation of alpha2 and beta1 waves was common for all extracts. According to previous studies, this is interpreted as activation of the dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission. In addition, Oenothera and Rhodiola extracts attenuated delta and theta power, probably related to interference with the cholinergic and norepinephrinergic transmission, respectively. Using discriminant analysis for comparison with reference pharmaceutical and botanical drugs, Rhodiola projected near the position of Ginkgo extract, whereas Oenothera extract was projected near the position of Tramadol, an analgesic drug. Physical motion was increased only in the presence of Paullinia extract and caffeine. Increases of longterm potentiation were observed in the presence of Rhodiola extract, Paullinia extract and caffeine.
The combined information predicts stimulant and cognitive function-enhancing activities in humans for the Rhodiola extract, which could also be used as a possible caffeine-replacement, and antidepressant and analgesic activity for the Oenothera extract.
Conclusion : In conclusion, the combination of Tele-Stereo-EEG in vivo and hippocampal slice preparation in vitro may be sufficient as a screening tool in order to gather enough pharmacological information to predict a clinical indication for herbal preparations anticipated to have CNS activity, especially when compared to a database of electropharmacograms for reference CNS-active pharmaceuticals.
Keywords : Pharmacology, Field Potentials, Hippocampal Slices, Rhodiola rosea, Oenothera paradoxa, Paullinia cupana, Caffeine, RhodioLife®, Discriminant Analysis.
Neuropharmacological Characterization of Extracts from Rhodiola rosea, Oenothera paradoxa and Paullinia cupana in Comparison to Caffeine - Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 2016, 7, 290-303 Published Online July 2016
Justus - Liebig - University Giessen, Giessen, Germany / NeuroCode AG, Wetzlar, Germany / NEKTIUM PoliNat Polifenoles Naturales, Las Palmas, Spain
Rhodiola rosea (and not crenulata) works on ATP and stimulates reparative energy
We studied the effects of oral treatment with extracts from Rhodiola rosea (50 mg/kg) and Rhodiola crenulata (50 mg/kg) roots on the duration of exhaustive swimming and ATP content in mitochondria of skeletal muscles in rats. Treatment with R. rosea extract significantly (by 24.6%) prolonged the duration of exhaustive swimming in comparison with control rats and rats treated with R. crenulata. R. rosea extract activated the synthesis or resynthesis of ATP in mitochondria and stimulated reparative energy processes after intense exercise. Experiments proved different pharmacological characteristics of R. rosea and R. crenulata: R. rosea is most effective for improving physical working capacity.
Rhodiola rosea (Crassulaceae) or golden root grows in Arctic highlands and is used for phytotherapy in Russia, Scandinavia, and Asia [5]. Extract of Rhodiola rosea root is characterized by stress-protective and antidepressive action. It alleviates emotional, mental, and physical disorders [10,11], reduces the severity of exhaustion after intensive physical exercise [1,4], elevates concentrations of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin in the brain, and acts as a nicotinic cholinergic agonist in the CNS [7]. Professional athletes use R. rosea for increasing physical activity, stimulating anabolic processes in skeletal muscles, increasing endurance during maximum physical exercise, and promoting subsequent recovery of the cardiovascular system.
We studied the effects of extracts from R. rosea roots and R. crenulata root on ATP content in the muscle mitochondria of rats before and after the exhaustive swimming test.
Results : R. rosea extract contained a complex of rosavines and salidroside (3.02% and 0.89% estimated for dry weight). The ratio of rosavines and salidroside in R. rosea root extract was 3:1, which is in line with published data [3]. R. crenulata extract contained only salidroside (2.05%).
The mean time until exhaustion was virtually the same in rats treated with R. crenulata and controls. Hence, R. crenulata root extract (in contrast to the R. rosea root extract) did not increase physical working capacity. Importantly, salidroside content in R. crenulata extract was 2.5 times higher than in R. rosea extract. Hence, the effects of R. rosea extract are due to the presence of rosavines and/or their complex with other compounds. ATP content in the mitochondria decreased after swimming exercise in controls and animals of both experimental groups. However, the decrease in ATP content in rats receiving R. rosea extract was less pronounced in comparison with not only the control, but also R. crenulata group. It can be hypothesized that R. rosea root extract more actively stimulated ATP synthesis or resynthesis in muscles during exercise.
Our findings indicate that R. rosea extract is characterized by unique pharmacological properties and produces a positive effect on ATP synthesis in mitochondria. R. rosea extract prolonged the duration of exhaustive swimming in rats and accelerated recovery after intensive exercise. The effects of R. rosea can be explained by the presence of rosavine complex, although the role of other bioactive compounds of this plant cannot be excluded.
Key Words: ATP; mitochondria; Rhodiola rosea; Rhodiola crenulata; rosavines; salidroside
Effet of Rhodiola extract on ATP content in Mitochondria of Skeletal Muscles [PTRHODIO3], Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, Vol. 136, No. 6, December, 2003, M. Abidov, F. Crendal, S. Grachev, R. Seifulla, and T. Ziegenfuss
Rhodilia anti-inflammatory on C-reactive protein and creatinine
The effects of extracts of Rhodiola rosea radix on blood levels of inflammatory C-reactive protein and creatinine kinase were studied in healthy untrained volunteers before and after exhausting exercise. Rhodiola rosea extract exhibited an antiinflammatory effect and protected muscle tissue during exercise.
Abstract : Professional athletes effectively use Rhodiola rosea (“golden radix”) extract as a safe nonsteroid food additive improving endurance and rapid recovery of muscles during several decades [7]. Rhodiola rosea extract improves muscle work due to mobilization and more economic expenditure of energy resources of muscles [1]. The use of adaptogens including R. rosea improved physical endurance of male athletes, reducing blood lactate level and accelerating recovery after exhausting exercise
Muscle injury involves inflammation (increase in blood IL-6 level) and increases the risk of myocardial infarction in subjects with latent cardiovascular diseases (particularly in those neglecting regular exercises) [9]. The inflammatory process plays an important role in the etiology of coronary disease. The relation- ship between increased blood concentrations of C-reactive protein (CRP) and creatinine kinase (CK) and muscle injuries in untrained subjects after exhausting physical exercise was demonstrated.
Here the effect of regular treatment with R. rosea extract and plasma levels of CRP and CK in untrained subjects before and after maximum exercise was evaluated in a double-blind placebo-controlled study.
Rsults : Exhausting physical muscle work appreciably increased CRP and CK levels in the blood of all volunteers (Table 1). This increase was less pronounced in group 1: 5 h after bicycle ergometer exercise CRP level in groups 2 and 3 increased 4-fold, while in group 1 only 2-fold. After 5 days the blood CRP levels in groups 2 and 3 remained increased (p max 0.05), while in group 1 it did not differ from the initial level. The mean CK level in the blood increased significantly after exhausting physical exercise (Table 1). Five hours after exercises this parameter was virtually the same in all groups. Five days after exercises CK activity in groups 2 and 3 further increased and 15- fold surpassed the initial level. In group 1 the blood CK content decreased and only 7-fold surpassed the initial level (Table 1). Hence, long-term treatment of untrained subjects with RHODAX inhibited the exhausting exercise-induced increase of the blood levels of substances serving as inflammationmarkers. RHODAX possesses antiinflammatory and, presumably, long-lasting adaptogenic effects. Two promising trends in the use of R. rosea extract can be outlined: facilitation of recovery after exercise and decrease of the risk of cardiological disorders.
Key Words: C-reactive protein; creatinine kinase; Rhodiola rosea; muscle protection; adaptogen
Rhodiola reduces the level of C-Reactive protein and Creatinine Kinase in the blood (Abidov, Grachev, ..) Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, No. 7, 2004 Pharmacology And Toxicology
Neuroprotection of Rhodiolife
We have shown that our proprietary Rhodiola rosea extract (RhodioLife) contains bioactives that are capable of stimulating gene modulation in brain cell cultures. In our model, the statistically significant expression of CALCRL, CDKN1A and LPAR2 suggests a potential role in neuroprotection. In silico evaluation of the molecular properties of the bioactives offers additional plausibility by showing a predicted favorable pharmacokinetic profile.
Rhodiola rosea, an adaptogen plant from cold regions, has been previously proposed for alleviating dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases. The goal of our study was to evaluate if our proprietary extract (Rhodiola RhodioLife) was able to elicit biological responses related to neuroprotection in neuronal cultures. NS20Y cells were cultured according to procedures and increasing concentrations of RhodioLife were added to the media. Viability at 24h using Presto BlueTM showed no statistically significant differences at those concentrations (0-50 ppm). Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis (G-coupled protein receptor [GCPR] array) showed statistically significant (p below 0.05) upregulation of 3 genes: calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A), and lysophosphatidic acid receptor 2 (LPAR2) (4, 3 and 2-fold respectively). In silico evaluation of the bioactives contained in RhodioLife (www.molinspiration.com) revealed that Salidroside, Rosarin, Rosavin, Rosiridin, Cinnamyl alcohol and p-Tyrosol all had 1 or no violations of the Lipinski´s rule of five, suggesting favorable pharmacokinetics. The predicted G-coupled protein receptor bioactivity was greatest for Rosarin (0.39) and Salidroside (0.35). We conclude that RhodioLife contained substances which had relevant biological activity and molecular properties suggesting a role in neuroprotection. Studies in suitable animal models are recommended.
Keywords: Neurodegenerative disease, Rhodiola rosea, G-coupled protein receptor, Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis
In Vitro and in Silico Evaluation of the Potential for Neuroprotection of Rhodiolife, A Rhodiola Rosea Roots Extract, Journal of Food Studies, Zubeldia, Hernández-Santana, Jiménez del Rio, Pérez-López, 2013, Vol. 2, No. 2
Reverse Mutation assay using bacteria with Rhodiola Rhodiolfe
It can be stated that during the described mutagenicity test and under the experimental conditions reported, Rhodiola Rhodiolife did not cause gene mutations by vbase pairs changes or frameshifts in the genome. Thereof, Rhodiola Rhodiolife is considered to be non-mutagenic in this bacterial reverse mutation assay.
The test item Rhodiola Rosea extract-5% rosavins (RHODIOLIFE) was investigated for its potential to induce gene mutations according to the plate incorporation test (experiment I) and the pre-incubation test (experiment II) using Salmonella typhimurium strains TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, TA 1537 and tester strain E. coli WP2 uvrA. In two independent experiments several concentrations of the test item were used. Each assay was conducted with and without metabolic activation. The concentrations, including the controls, were tested in triplicate.
Bacterial reverse mutation assays use amino-acid requmng strains of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) to detect point mutations, which involve substitution, addition or deletion of one or a few DNA base pairs. The principle of these bacterial reversion assays is that they detect mutations which functionally reverse mutations present in the tester strains and restore the capability to synthesise an essential amino acid (1), (3), (6). The purpose of this study is to establish the potential of the test item to induce gene mutations in bacteria by means of a S. typhimurium and E. coli reverse mutation assay. There is no requirement for verification of a clear positive response. Equivocal results should be clarified by further testing preferably using a modification of experimental conditions. Negative results need to be confirmed on a case-by-case basis. Modification of study parameters to extend the range of conditions assessed should be considered in follow-up experiments. Study parameters that might be modified include the concentrations spacing and / or the method of treatment (pre-incubation method). In case of severe toxicity of the test item or the use of ethanol as the most appropriate solvent the confirmatory experiment is carried out according to the plate incorporation method with a different spacing between dose levels.
In conclusison, it can be stated that during the described mutagenicity test and under the experimental conditions reported, Rhodiola Rhodiolife did not cause gene mutations by vbase pairs changes or frameshifts in the genome. Thereof, Rhodiola Rhodiolife is considered to be non-mutagenic in this bacterial reverse mutation assay.
Reverse Mutation assay using bacteria with Rhodiola Rhodiolfe - this is a internal document aailable upon specific
request and need.
Pioneering cultivation program boosts adaptogen sustainability
Nektium takes steps to ensure the long-term sustainability of its Rhodiola rosea extract Rhodiolife®
Nektium is taking steps to secure the long-term sustainability of its Rhodiolife® Rhodiola rosea extract by switching a significant proportion of its raw material sourcing to cultivated plants. The move – an industry first on such a large commercial scale – will reduce reliance on under-pressure wild-grown supplies.
Rhodiola rosea is one of the most powerful adaptogens found in nature, offering a range of cognitive and sports nutrition benefits. It grows wild in the remote Altai mountains in south and central Asia at the intersection of Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China. The rapidly growing market for adaptogens has increased demand for Rhodiola rosea roots, leading to concerns about over-harvesting.
In response, Nektium has worked with its long-standing local partner to establish fields that offer conditions optimal for the controlled growing of Rhodiola rosea. Together, they have converted barren land in undeveloped, unpopulated locations, ensuring minimal impact on communities close by. After a successful trial, initial exploratory fields were extended to provide full-scale sustainable cultivation sufficient to satisfy market demand at an industrial level. The plant material used to grow Nektium’s cultivated Rhodiola rosea for Rhodiolife® was originally taken from wild-harvested Siberian plants growing near where the fields have been established. This means there are no physical or phytochemical differences between Rhodiolife® produced from wild-harvested roots and that produced from cultivated raw materials. As a responsible supplier of botanical ingredients, Nektium is acutely aware of the importance of conservation, and this initiative will help to secure a sustainable and reliable source of Rhodiola rosea roots for years to come. In addition, cultivation in a controlled setting results in a more predictable and secure long-term raw material supply, which leads to improved price stability, superior safety, and more effective quality control. It also offers greater peace-of-mind around authenticity, which is especially significant in an age of widespread adulteration.
Genotoxicity of Rhodiola rosea Rhodiolife
Nektium can so offer the gentox studies (available upon specific request) which is something EMEA highlighted as a negative issue in their assessment.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects ot Rhodiola rosea extract from Nektium in the in vitro micronucleus assay. This document is a confidential document, and belongs to Nektium for Rhodiolife exclusively.
Transitioning from wild-harvest to sustainable cultivation
Conscious about the pressure on the demand of Rhodiola rosea, Nektium took action to preserve the conservation status of its wild populations. To that extend, some years ago we started an initiative to organize and deploy cultivation fields together with our long-standing partners.
It's become Nektiums priority to preserve Rhodiola rosea in its natural environment, given that the IUCN* red list has already flagged Rhodiola rosea. The cultivation efforts relieve harvesting pressure on wild growing plants and reduce the threat of extinction of Rhodiola roseain some areas.Transitioning from wild-harvest to cultivation is based on the vision on:
●Sustainability
●Reliable supply
●Crop management
●Authenticity and traceability
●Safety
●Quality
●Social impact
The location of farms was carefully selected to preserve the original features of Rhodiola rosea rosea. In fact, the cultivated plants are fully adapted, as climatic conditions are the same as the ones they enjoy in wild nature. Through the cultivation of Rhodiola rosea, Nektium :
●can guarantee sustainable and sustained supply of raw material.
●Have a better control over volumes on the long long-term
●Are able to ensure price stability for customers on the longlong-term
●Ensure correct identification of plant material/ avoid adulteration
●Counteract the increasing scarcity of plant material in nature
Nektium´s ID Assessment Program on Rhodiolife to guarantee only Rhodiola rosea
Because customers wish to get Rhodiola rosea - and only, without even traces of other species - Nektium applies multiple complementary analytical methodologies, selecting the most appropriate test for each step: Identification, Quality Control, and Traceability
Because customers wish to get Rhodiola rosea - and only, without even traces of other species -
Macroscopic ID
●Visual and organoleptic characterization
●Morphological analysis
●Identification with authenticated or in-house plant reference material
DNA barcode
●Isolate DNA from plant
●Amplify DNA by PCR
●Sequence PCR product
●Analysis performed by accredited 3rd party laboratories
HPLC fingerprint
●Validated HPLC-DAD methods
●Primary analytical standards for ID
●ID matching of phytochemical profiles: raw material and final product
HPTLC
●Photo-Documentation
●ID matching: raw material and botanical extracts Validated HPTLC test methods
●Analysis performed by accredited 3rd party laboratories
Freeze-dried Rhodiolife in prolonging physical exertion
The FDE-treated group showed greater plasma corticosterone reduction, spared more muscle glycogen, and had higher levels of plasma fatty acids than the SDE group, clearly revealing superiority in all three biochemical parameters. Thus, the relatively brief exposure of R. rosea root extract to heat during the spray-drying process is sufficient to reduce its performance-enhancing properties. The isolation and identification of heat-sensitive component(s) will be the subject of our future investigation.
Rhodiola rosea L (Crassulaceae) is anabolic and adaptogenic phytomedicine traditionally used in Russia to improve mental and physical health. The effect of freeze-dried extract (FDE) and spray-dried extract (SDE) of R.rosea root, both standardized to minimum 3.0% rosavins and 0.8% salidroside, was comparatively tested using the swimming time to exhaustion (STE) test in rats. Plasma fatty acids, corticosterone, and muscle glycogen concentrations were monitored in three experimental groups corresponding to each form of the extract and a control group, which received only maltodextrin. The FDE-treated group (50mg/kg) was able to swim 43.1 +/-5.5% longer that the control group (50mg/kg, Pbelow 0.05), and more significantly, 27.8 + 3.2% longer than the SDE-treated group (50mg/kg, P below 0.05). Furthermore, after a 30-minute rest, the FDE-treated animals recovered much quicker and were able to swim for an average of 3.9+0.6 additional minutes (37.5+3.7% extra swimming time) compared to the SDE group, and 7.7+0.8 minutes (74.0+3.2% extra swimming time) compared to the control group. The FDE-treated group showed greater plasma corticosterone reduction, spared more muscle glycogen, and had higher levels of plasma fatty acids than the SDE group, clearly revealing superiority in all three biochemical parameters. Thus, the relatively brief exposure of R. rosea root extract to heat during the spray-drying process is sufficient to reduce its performance- enhancing properties. The isolation and identification of heat-sensitive component(s) will be the subject of our future investigation.
Freeze-dried Rhodiola rosea extract demonstrates a two-fold advantage in prolonging physical exertion in rats, compared to the spray-dried form, Musa T. Abidov), R. Steven Sikorski, Arthur Z. Ramazanov, Miguel Jimenez del Rio
Rhodiola rosea Rhodiolife - Standardized formula for sustained energy
The preclinical evaluation of spray-dried-extract (SDE) and freeze- dried-extract (FDE) demonstrated significantly more effective in stimulating greater physical endurance and enhancing the recovery time from intensive workout
The efficacy of an adaptogen in increasing the body’s non-specific resistance (NSR) to stress depends on the dynamics of its biological action and standardization of the botanical or mineral extract. The time of the onset of action of an adaptogen may vary, and the local or systemic beneficial effects of the adaptogen’s use may wear off with time. The adaptogen mechanism of Rhodiola rosea is characterized by a rapid onset of action, within days, and subsequent sustained delivery of a non-specific resistance to stress. This mechanism is due to Rhodiola’s broad action that increases resistance to stress in the central nervous, immunological, cardio-pulmonary and endocrine systems. The biological activity of Rhodiola root extract is highly dependent upon the method of extraction and drying of the extract. The preclinical evaluation of spray-dried-extract (SDE) and freeze- dried-extract (FDE) demonstrated significantly more effective in stimulating greater physical endurance and enhancing the recovery time of animals from intensive workout, as compared to the SDE. The extract provides a spectrum of active components corresponding to ratios found in the native Rhodiola root, i.e. the natural ratio of rosavins/salidroside ranging approximately from 1.3 to 3. The biologically effective extract of the roots shows that the HPLC peaks for the active ingredients salidroside, tyrosol, rosarin, rosavin, rosaridin and rosavinol overlap with the HPLC pattern of the native root.
Rhodiola rosea Rhodiolife - Standardized formula for sustained energy : V. Badmaev, S. Rosenbush, E. Anderson, M. Jimenez, B. Pacchetti, J.Liedek, K. Morimoto
New Rhodiolife Applications based on animal EEG studies
Rhodiolife® is a proprietary extract of Rhodiola rosea, standardized to total rosavins (up to 5%) and salidrosides (up to >1.8%), developed by Nektium. The EEG signature of Rhodiolife® was compared to the EEG signatures of other stimulant products tested under identical conditions. Leaflet.
Rosavins and salidrosides have anti-oxidant, ant-infl ammatory, anti-viral, anti-fatigue and anti-aging properties. As an adaptogen, Rhodiola rosea reduces depression and anxiety and supports the immune system. In earlier studies we successfully demonstrated that Rhodiolife® protects muscle cells against peroxide-induced oxidative stress, increases mitochondrial ATP level, improves physical work capacity and the recovery after vigorous physical exercise, is anti-infl ammatory, protects muscle tissue of healthy untrained volunteers during exercise and avoids virus reproduction during the sensitive period of low immuneresistance right after intensive exercise.
Recently, we studied Rhodiolife® for CNS activity in four diff erent brain regions in vivo by Electroencephalogram (EEG) and discovered surprising stimulant and mental energy activity, giving insight into entirely new applications for Rhodiolife®. Administration of a single dose of Rhodiolife® at 100mg/kg led to surprisingly marked CNS stimulant activity which lasted the entire recording period of 5 hours. The EEG signature of Rhodiolife® was compared to the EEG signatures of other stimulant products tested under identical conditions, and surprisingly, the stimulant activity of Rhodiolife® was comparable to that of caffeine and guarana and indicating Rhodiolife® will be suitable for improvement of cognitive function.
Rhodiola rosea, Versatile Adaptogen
There is immense potential to develop health foods, foods supplements, herbal preparations, and drugs from this unique herb from high altitudes. Its potential for development of radioprotectants—needed in today’s world— is immense. Promotion of its production and protection would be beneficial to society.
Abstract : Rhodiola rosea (rose root) belonging to the family Crassulaceae is a popular medicinal plant in Russia, Scandinavia, and many other countries. Extracts of the roots of this plant have been found to favorably affect a number of physiological functions including neurotransmitter levels, central nervous system activity, and cardiovascular function. It is being used to stimulate the nervous system, decrease depression, enhance work performance, eliminate fatigue, and prevent high-altitude sickness. Most of these effects have been ascribed to constituents such as salidroside (rhodioloside), rosavins, and p-tyrosol. It has also been found to be a strong antioxidant and anticarcinogen due to the presence of several phenolic compounds. Adaptogens are plant extracts that allow an organism to counteract adverse physical, chemical, and biological stressors by generating nonspecific resistance. Adaptogens are known to increase the availability of energy during the day, reduce stressed feelings, increase endurance, and increase mental alertness. This multipurpose medicinal plant (R. rosea), with adaptogenic properties that increase the body’s nonspecific resistance and normalize functions, has been traditionally grown and used in Russia and Mongolia. Due to increasing consumer demands toward natural health products and the growing interests in the secondary metabolites of plants and their application in biotechnology and therapy, much focus has been put on the rose root and its medical properties. The rose root imparts normalizing influences on adverse physical, chemical, and biological disturbances but is otherwise innocuous. In India, the plant has been growing wild in the high altitudes of the Himalayas. The Defence Research and Development Organization in India has taken on the responsibilities of its conservation, as well as the development of multiple management practices and the development of health foods, supplements, and nutraceuticals in India.
Introduction : Controlled studies are warranted to explore its use in antidepressant augmentation, disorders of memory and cognition, attention deficit disorder, traumatic brain injury, Parkinson’s disease, protection against arrhythmias, sports performance, aviation and space medicine (enhancing physical and mental performance while reducing stress reactions), endocrine disorders (infertility, premenstrual disorder, menopause), sexual dysfunction, disorders of the stress-response system (fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, and posttraumatic stress disorder), and enhancement of chemotherapy/radiation with amelioration of toxicity.
During evolution, R. rosea has adapted to the harsh conditions of high altitude (extreme cold, low oxygen, little rainfall, and intense irradiation from the sun) by producing a group of powerful protective compounds that have diverse beneficial effects in animals and humans. One is struck by the versatility of R. rosea, from its description in Greek medicine 2000 y ago to its use by 21stcentury cosmonauts. It is time for modern research, using controlled clinical trials, to develop the potential medical applications for this unique phyto-adaptogen. There is immense potential to develop health foods, foods supplements, herbal preparations, and drugs from this unique herb from high altitudes. Its potential for development of radioprotectants - needed in today’s world - is immense. Promotion of its production and protection would be beneficial to society.
Conclusion (partial) There is immense potential to develop health foods, foods supplements, herbal preparations, and drugs from this unique herb from high altitudes. Its potential for development of radioprotectants—needed in today’s world— is immense. Promotion of its production and protection would be beneficial to society.
Controlled studies are warranted to explore its use in antidepressant augmentation, disorders of memory and cognition, attention deficit disorder, traumatic brain injury, Parkinson’s disease, protection against arrhythmias, sports performance, aviation and space medicine (enhancing physical and mental performance while reducing stress reactions), endocrine disorders (infertility, premenstrual disorder, menopause), sexual dysfunction, disorders of the stress-response system (fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, and posttraumatic stress disorder), and enhancement of chemotherapy/radiation with amelioration of toxicity. During evolution, R. rosea has adapted to the harsh conditions of high altitude (extreme cold, low oxygen, little rainfall, and intense irradiation from the sun) by producing a group of powerful protective compounds that have diverse beneficial effects in animals and humans.
Rhodiola rosea: A Versatile Adaptogen - Farhath Khanum, Amarinder Singh Bawa, and Brahm Singh, 2005 Institute of Food Technologists, Vol. 4, 2005
Antiviral effects of salidroside from Rhodiola rosea L
The aim of this study was to investigate the antiviral effects of salidroside, a major component of Rhodiola rosea L.
The aim of this study was to investigate the antiviral effects of salidroside, a major component of Rhodiola rosea L. First, the antiviral effects of salidroside against coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) were determined in vitro and in vivo. Then, the effect of salidroside on the mRNA expression of some important cytokines was measured in hearts of infected BALB/c mice by RT-PCR. Salidroside exhibited obvious antiviral effects both in in vitro and in vivo experiments. Salidroside was found to modulate the mRNA expression of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-2 (IL-2). In conclusion, salidroside possesses antiviral activities against CVB3 and it may represent a potential therapeutic agent for viral myocarditis.
(...to be continued)
The in vitro and in vivo antiviral effects of salidroside from Rhodiola rosea L. against coxsackievirus B3, Copyright © 2008 Elsevier GmbH - Haibo Wang, Yuanyuan Ding, Jun Zhou, Xiaoli Sun, Siwang Wang
Adaptogenic and CNS Effects of Rhodiola rosea
This study thus provides evidence of the efficacy of R. rosea extracts after a single administration, and confirms many preclinical and clinical studies indicating the adaptogenic and stimulating effects of such R. rosea extracts. Moreover, antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like activities of R. rosea were shown in mice for the first time.
Rhodiola rosea L., or ‘golden root’, is a popular plant in traditional medicine in Eastern Europe and Asia, with a reputation for improving depression, enhancing work performance, eliminating fatigue and treating symptoms of asthenia subsequent to intense physical and psychological stress. Due to these therapeutic properties, R. rosea is considered to be one of the most active adaptogenic drugs. To confirm and extend results obtained in the few preclinical and clinical studies available in English language journals, the purpose of the present study was to re-investigate the effects produced by a single oral administration of an R. rosea hydroalcohol extract (containing 3% rosavin and 1% salidroside) on the central nervous system in mice. The extract was tested on antidepressant, adaptogenic, anxiolytic, nociceptive and locomotor activities at doses of 10, 15 and 20 mg/kg, using predictive behavioural tests and animal models. The results show that this R. rosea extract significantly, but not dose-dependently, induced antidepressant-like, adaptogenic, anxiolytic-like and stimulating effects in mice. This study thus provides evidence of the efficacy of R. rosea extracts after a single administration, and confirms many preclinical and clinical studies indicating the adaptogenic and stimulating effects of such R. rosea extracts. Moreover, antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like activities of R. rosea were shown in mice for the first time.
(...to be continued)
Adaptogenic and Central Nervous System Effects of Single Doses of 3% Rosavin and 1% Salidroside Rhodiola rosea L. Extract in Mice, Marina Perfumi and Laura Mattioli, PHYTOTHERAPY RESEARCH
AChE Inhibitors in Rhodiola rosea.
In view of this plants ability to inhibit AChE and cause memory improvement at levels which do not cause detectable side effects, the extract of Rhodiola rosea should be examined for its effectiveness at treating memory impairments such as those caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
Abstract : The alcohol extract or Rhodiola rosea has been shown to cause 42 +/- 3.2% inhibition of acetyl- choline esterase (AChE) when tested at 10g/L. This AChE inhibition provides a physiological explanation for the reported mental and memory enhancing properties of Rhodiola rosea extracts. Active guided fractionation indicated a multitude of components which are responsible for this plants AChE inhibition. Two flavonoid glycosides (gossypetin- 7-O- L- rhamnopyranoside and rhodio-flavonoside) were isolated and shown to cause 58 +/- 15% and 38 +/- 4% AChE inhibition respectively when tested at 5g/L. In view of this new enzymatic activity and previous clinical work indicating memory and mental enhancing properties with no indication of toxicity, this plant needs to be researched for its potential at treating memory impairing disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Conclusion : In conclusion, the alcoholic extract of Rhodiola rosea has been shown to cause moderate inhibition of acetylcholine esterase. This plant appears to contain a multitude of different AChE inhibitors including gossypetin-7-O-Lrhamnopyranoside and rhodioflavonoside. In view of this plants ability to inhibit AChE and cause memory improvement at levels which do not cause detectable side effects, the extract of Rhodiola rosea should be examined for its effectiveness at treating memory impairments such as those caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
Keywords: Rhodiola rosea gossypetin-7-O-l- rhamnopyranoside rhodioflavonoside acetylcholine esterase AChE
(...to be continued)
Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors in Rhodiola rosea. Brian Hillhouse,Dong Sheng Ming,Christopher French &G.H. Towers. Pharmaceutical Biology 2004, Vol. 42, No. 1, pp. 68–72
Rhodiola rosea for sensitive skin care
Results show a significant increase in opioid peptides release, an inhibitory effect on neuropeptides production, and modulation of cytokines production by keratinocytes under ultraviolet stress.
Background ; The pathophysiology of sensitive skin consists of an inflammatory reaction resulting from the abnormal penetration in the skin of potentially irritating substances, which occurs due to skin barrier dysfunction and changes in the production of local neuromediators.
Aims The therapeutic potential of l -carnosine and Rhodiola rosea , as antioxidant and neuromodulatory, respectively, leads us to investigate the effects of the R. rosea extract/ l - carnosine–associated compound (RCAC) on sensitive skin alterations.
Methods A double-blind comparative study was conducted on 124 volunteers with sensitive skin, who were selected by their reactivity to stinging test. Two randomized groups of 62 each received either a formulation containing 1% of RCAC or placebo, which was applied twice a day for 28 consecutive days. One perceptibility questionnaire was applied at the onset and at the end of the treatment to evaluate the subjective response to test product. Additionally, in vitro studies were performed to investigate RCAC neuroimmunomodulatory mechanisms.
Results RCAC treatment produced in vivo protective effects in skin barrier function and a positive subjective response of sensitive skin volunteers. In vitro treatment promoted the release of proopiomelanocortin peptides and restored to normal the increased levels of neuropeptides and cytokines produced by keratinocytes exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Clinical effectiveness was measured by reduction of transepidermal water loss, positive perceptions of improvements in skin dryness and skin comfort sensation, and reduction of discomfort sensation after stinging test.
Conclusions The protective effect of RCAC in skin barrier function and the positive response produced in human subjects with sensitive skin could be partially explained by our in vitro results showing a significant increase in opioid peptides release, an inhibitory effect on neuropeptides production, and modulation of cytokines production by keratinocytes under ultraviolet stress.
Keywords : cytokines, neuroimmunomodulation, proopiomelanocortin peptides, sensitive skin, stinging test, transepidermal water loss
Neuroimmunomodulatory compound for sensitive skin care: in vitro and clinical assessment Gustavo de Campos Dieamant, Maria Del Carmen Velazquez Pereda, Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 7, 112–119
Green tea, Rhodiola, Magnesium and B vitamins modulates brain activity
Effects of a combination of green tea, rhodiola, vitamins B and magnesium in 100 moderately stress healthy adults. volunteers experiencing social stress. The combined treatment significantly increased EEG resting state theta - considered indicative of a relaxed, alert state, attenuated subjective stress, anxiety and mood disturbance. Therefore, the combination may reduce the effects of social stress in healthy subjects
BACKGROUND: Magnesium (Mg), green tea and rhodiola extracts have, in isolation, been shown to possess stress and anxiety relieving effects. Green tea and rhodiola have been shown to modulate EEG oscillatory brain activity associated with relaxation and stress perception. The combined capacity of these ingredients to confer protective effects under conditions of acute stress has yet to be examined. We tested the hypothesis that a combination of Mg (with B vitamins) + green tea + rhodiola would acutely moderate the effects of stress exposure.
METHODS: A double blind, randomised, placebo controlled, parallel group design was employed (Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT03262376; 25/0817). One hundred moderately stressed adults received oral supplementation of either (i) Mg + B vitamins + green tea + rhodiola; (ii) Mg + B vitamins + rhodiola; (iii) Mg + B vitamins + green tea; or (iv) placebo. After supplementation participants were exposed to the Trier Social Stress Test. The effects of the study treatments on electroencephalogram (EEG) resting state alpha and theta, subjective state/mood, blood pressure, heart rate variability and salivary cortisol responses after acute stress exposure were assessed.
RESULTS: The combined treatment significantly increased EEG resting state theta (p max .02) - considered indicative of a relaxed, alert state, attenuated subjective stress, anxiety and mood disturbance, and heightened subjective and autonomic arousal (p max .05).
CONCLUSIONS: Mg, B vitamins, rhodiola and green tea extracts are a promising combination of ingredients that may enhance coping capacity and offer protection from the negative effects of stress exposure.Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03262376.
A combination of green tea, rhodiola, magnesium and B vitamins modulates brain activity and protects against the effects of induced social stress in healthy volunteers, Neil Bernard Boyle , Jac Billington , Clare Lawton , Frits Quadt , Louise Dye, Nutr Neurosci 2021 Apr 26
Rhodiola rosea on exercise performance and cognitive function
Acute Rhodiola rosea ingestion decreases the heart rate response to sub-maximal exercise, and appears to improve endurance exercise performance
Background The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of an acute oral dose of 3 mg/kg of Rhodiola rosea (R. rosea) on endurance exercise performance, mood, and cognitive function.
Methods A total of 15 recreationally active college women (21.3 ± 0.09 y, 56.1 ± 6.3 kg; mean ± SD) participated in this study. 2–7 d after a familiarization trial subjects ingested in a double blind, random crossover manner, either R. rosea or a carbohydrate placebo 1 h prior to testing. Exercise testing consisted of a 10 minute warm-up, standardized to 80% of the average watts produced during the familiarization trial, followed by a 6 mile simulated indoor time trial on a Velotron electronic bicycle ergometer. Every 5 min during the time trial, subjects rated their level of perceived exertion using a BORG 10 pt scale. A blood sample was taken pre warm-up, 2 minutes post warm-up, and 2 minutes following completion of the time trial, and was analyzed for lactate concentration. Subjects also completed a Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaire and a Stroop's color test pre-warm up and following the completion of the time trial. Subjects returned to the lab 2–7 d later to repeat the testing with the other condition.
Results A 3 mg/kg acute does of R. rosea resulted in a shorter time to completion of the 6 mile time trial course (R. rosea 1544.7 ± 155.2 s, Placebo 1569.5 ± 179.4 s; mean ± SD; p = 0.06) as well as a lower average heart rate during the standardized warm up (R. rosea 138.6 ± 13.3 bpm, Placebo 143.7 ± 12.4 bpm; mean ± SD; p = 0.001). There were no significant differences between treatment conditions for rating of perceived exertion during the time trial. Both treatments resulted in a significant increase in the POMS fatigue score following exercise (p = 0.001), as well as a significant improvement following exercise for the Stroop's test of incongruent words (p = 0.001). No other significant differences between treatments were observed.
Conclusion Acute Rhodiola rosea ingestion decreases the heart rate response to sub-maximal exercise, and appears to improve endurance exercise performance.
The effects of an acute dose of Rhodiola rosea on exercise performance and cognitive function, Eric Noreen, James Buckley and Stephanie Lewis, Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition 2009, 6(Suppl 1):P14
Rhodiola rosea extracts on cellular immunity
The aim of our work was to study in vitro and in vivo the effects of aqueous and 50% hydroalcoholic extracts of Rhodiola rosea on non-specific and specific cellular immunity in pigs, rats and mice.
Abstracts : The genus Rhodiola (Crassulaceae) consists of more than 100 species growing mainly in Asia and Europe. The best known is Rhodiola rosea. The roots of this species are traditionally used as a tonic, adaptogen, antidepressant and anti-inflammatory drugs. The aim of our work was to study in vitro and in vivo the effects of aqueous and 50% hydroalcoholic extracts of Rhodiola rosea on non-specific and specific cellular immunity in pigs, rats and mice. Mice were fed 50, 100, 200, or 400 μg of Rhodiola extracts daily, for 7 days before cellular immunity study (local GVH reaction). Blood leukocytes collected from pigs and rats were cultivated in vitro with PHA or LPS in the presence of 1-50 μg/ml of Rhodiola rosea extracts for 72 hours.
The metabolic activity of blood phagocytes (mostly granulocytes) was determined based on the measurement of intracellular respiratory burst after stimulation by PMA (phorbol myristate acetate), and potential bactericidal activity was determined in isolated blood leukocytes stimulated with microorganisms. Additionally, some in vitro toxicological studies were performed. For these experiments GMK (monkey’s kidney), EPC (fish epithelial cells), and KFC (Koy fins cells) cell lines, as well as lymphocytes and monocytes isolated from the blood of pigs and rats were used.
Both extracts enhanced non-specific and specific cellular immunity to the various degrees; however, in higher doses or concentrations they presented inhibitory effects. In in vitro studies all extracts were non-toxic at concentrations 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, and 1000 μg/ml after 24, 48, and 72 hours of cells cultures.
Key words: pigs, rats, mice, Rhodiola rosea, cellular immunity
The influence of Rhodiola rosea extracts on non-specific and specific cellular immunity in pigs, rats and mice, Central European Journal of Immunology 2007; 32 (2), Andrzej K. Siwicki , Ewa Skopinska-Roewska, Malgorzata Hartwich, roman Wojcik, Tadeusz Baku, Mirosawa Furmanowa, Barbara J. BaLan, ewa Sommer
Anti-inflammatory activity of Rhodiola rosea
Inhibition of nystatin induced oedema and phospholipase A2 suggested that membrane stabilization could be the most probable mechanism of action of RTE in anti-inflammation. The findings in this study may provide the use of R. rosea root extract in the treatment of inflammatory conditions.
Rhodiola rosea (golden root), a unique phytoadaptogen grown in high-altitude regions has gained attention for its various therapeutic properties. In India, this plant is found in the Himalayan belt and has not been completely explored for its beneficial health effects. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the anti-inflammatory efficacy of the tincture extract of Rhodiola rosea roots (RTE). The anti-inflammatory activity was determined through carrageenan-induced paw oedema, formaldehyde-induced arthritis and nystatin-induced paw oedema in rat model. The tincture extract exhibited inhibitory effect against acute and subacute inflammation at a dose of 250 mg/kg body weight. Inhibition of nystatin-induced oedema was also observed in a dose-dependent manner. The in vitro inhibitory effects of the tincture extract from R. rosea roots was evaluated against the enzymes relating to inflammation. The enzymes include cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Phospholipase A2 (PLA2). The extract showed varying inhibitory activities against these enzymes depending on the concentrations. A potent inhibition was observed against Cox-2 and PLA2. Inhibition of nystatin induced oedema and phospholipase A2 suggested that membrane stabilization could be the most probable mechanism of action of RTE in anti-inflammation. The findings in this study may provide the use of R. rosea root extract in the treatment of inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: Rhodiola rosea; anti-inflammatory activity; cyclooxygenases-1 and 2; phospholipase A2: membrane stabilization.
Anti-inflammatory activity of Rhodiola rosea – “a second-generation adaptogen”, Pooja, A. S. Bawa and Farhath Khanum, Phytother. Res. 23, 1099–1102 (2009)
Rhodiola rosea - a possible plant adaptogen
Rhodiola rosea has been categorized as an adaptogen by Russian researchers due to its observed ability to increase resistance to a variety of chemical, biological, and physical stressors. Its claimed benefits include antidepressant, anticancer, cardioprotective, and central nervous system enhancement.
Abstract Rhodiola rosea is a popular plant in traditional medical systems in Eastern Europe and Asia with a reputation for stimulating the nervous system, decreasing depression, enhancing work performance, eliminating fatigue, and preventing high altitude sickness. Rhodiola rosea has been categorized as an adaptogen by Russian researchers due to its observed ability to increase resistance to a variety of chemical, biological, and physical stressors. Its claimed benefits include antidepressant, anticancer, cardioprotective, and central nervous system enhancement. Research also indicates great utility in asthenic conditions (decline in work performance, sleep difficulties, poor appetite, irritability, hypertension, headaches, and fatigue) developing subsequent to intense physical or intellectual strain. The adaptogenic, cardiopulmonary protective, and central nervous system activities of Rhodiola rosea have been attributed primarily to its ability to influence levels and activity of monoamines and opioid peptides such as beta-endorphins.
Rhodiola rosea: A Possible Plant Adaptogen Gregory S. Kelly, Altern Med Rev 2001;6(3):293-302)
Plants chemistry and biological activity of Rhodiola rosea
This review article summarizes the bioactivities, including adaptogenic, antifatigue, antidepressant, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antinoception, and anticancer activities, and the modulation of immune function of Rhodiola plants and its constituents, as well as their potential to prevent cardiovascular, neuronal, liver, and skin disorders.
Rhodiola is a genus of medicinal plants that originated in Asia and Europe and are used traditionally as adaptogens, antidepressants, and anti-inflammatory remedies. Rhodiola plants are rich in polyphenols, and salidroside and tyrosol are the primary bioactive marker compounds in the standardized extracts of Rhodiola rosea. This review article summarizes the bioactivities, including adaptogenic, antifatigue, antidepressant, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antinoception, and anticancer activities, and the modulation of immune function of Rhodiola plants and its two constituents, as well as their potential to prevent cardiovascular, neuronal, liver, and skin disorders.
Keywords: bioactivity Rhodiola salidroside tyrosol
Rhodiola plants: Chemistry and biological activity, Hsiu-Mei Chiang, Hsin-Chun Chen, Journal of Food And Drug Analysis, 2015
Salidroside and Immune responses
The result showed that salidroside liposome formulation not only could promote the maturation of DCs, the stimulation of DCs on MLR proliferation and the antigen presenting ability, but also induced the sustained cellular immune and humoral immune response.
Salidroside liposome formulation enhances the activity of dendritic cells and immune responses : Salidroside, the important composition, of Rhodiola rosea L. has been reported to have various pharmacological properties. Liposome is known to be effective as drug carriers and immune adjuvant. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate immunological adjuvant activity of salidroside liposome. Here we reported the preparation, the effect on DCs in vitro and the immune response in vivo. The immunological adjuvant activity of salidroside liposome formulation was compared with that of salidroside and liposome. The result showed that salidroside liposome formulation not only could promote the maturation of DCs, the stimulation of DCs on MLR proliferation and the antigen presenting ability, but also induced the sustained cellular immune and humoral immune response. Overall, the results showed that salidroside liposome formulation had the potential to act as effective sustained release vaccine delivery systems.
(...to be continued)
Salidroside liposome formulation enhances the activity of dendritic cells and immune responses. Xiaojuan Zhao, Yu Lu, Yang Tao, Yee Huang, Deyun Wang, Yuanliang Hu, Jiaguo Liu, Yi Wu, Yun Yu, Cui Liu. PMID: 24188805 DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.10.016
Putative botanical antidepressant
R. rosea demonstrates multi-target effects on various levels of the regulation of cell response to stress, affecting various components of the neuroendocrine, neurotransmitter receptor and molecular networks associated with possible beneficial effects on mood
Background: Rhodiola rosea ( R. rosea ) is a botanical adaptogen with putative anti-stress and antidepres- sant properties. Evidence-based data supporting the effectiveness of R. rosea for depression in adults is limited, and therefore a comprehensive review of available animal and human studies suggesting a puta- tive antidepressant action is warranted. Purpose: A review of the literature was undertaken to ascertain studies of possible antidepressant mech- anisms of action and studies of the safety and effectiveness of R. rosea extracts in animals and adult humans. Methods: A search of MEDLINE and the Russian state library database was conducted (up to October 2015) on R. rosea . Results: Mechanism of action: R. rosea extracts and its purified constituent, salidroside, has been shown to produce a variety of mediator interactions with several molecular networks of neuroendocrine-immune and neurotransmitter receptor systems likely to be involved in the pathophysiology of depression. A wide variety of preclinical in vivo and ex vivo studies with laboratory animals suggests the presence of several biochemical and pharmacological antidepressant-like actions. Effectiveness: Clinical assessment of R. rosea L. rhizome extracts in humans with various depressive syn- dromes is based upon results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of 146 sub- jects with major depressive disorder and seven open-label studies totaling 714 individuals with stress- induced mild depression (diagnosed as asthenic syndrome or psychoneurosis). Overall, results of these studies suggests a possible antidepressant action for R. rosea extract in adult humans. Safety: In contrast to most conventional antidepressants, R. rosea extract appears to be well-tolerated in short-term studies with a favorable safety profile. Conclusions: R. rosea demonstrates multi-target effects on various levels of the regulation of cell response to stress, affecting various components of the neuroendocrine, neurotransmitter receptor and molecular networks associated with possible beneficial effects on mood .
Keywords: Rhodiola rosea L., Depression Clinical study Pharmacology Molecular networks
Rhodiola rosea L. as a putative botanical antidepressant, Jay D. Amsterdam, Alexander G. Panossian, Phytomedicine 23 (2016) 770–783
Rejuvenating activity of salidroside
These indicate that SDS is able to counteract immunosenescence, thereby resulting in rejuvenation. Practically, SDS may be used to help the elderly to generate an improved response to vaccine with stronger humoral and cell-mediated immune responses.
It is well known that immune response decreases with aging. Salidroside (SDS), an antioxidant component isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine roseroot Rhodiola rosea, has been demonstrated to possess potent anti-aging and health-promoting activities. However, the mechanism underlying these activities is poorly understood. In this study, we clearly demonstrated that (1) dietary intake of SDS induced a considerable increase in total T cells (CD3(+)) and T helper cells (CD4(+)) in aged (21 months old) Wistar male rats; (2) SDS supplementation significantly increased the DTH response, a T cell-mediated immune response, in aged rats; and (3) SDS supplementation remarkably promoted the production of total anti-KLH IgG, anti-KLH IgG1, and anti-KLH IgG2α in aged rats without disturbing immune homeostasis. These indicate that SDS is able to counteract immunosenescence, thereby resulting in rejuvenation. Practically, SDS may be used to help the elderly to generate an improved response to vaccine with stronger humoral and cell-mediated immune responses.
Keywords Rats . Salidroside . Ageing . Anti-ageing . Immune response
Rejuvenating activity of salidroside (SDS): dietary intake of SDS enhances the immune response of aged rats. Linlin Lu & Jiangshui Yuan & Shicui Zhang
Acute Rhodiola Rosea Intake Can Improve Endurance Exercise Performance
Acute Rhodiola rosea intake can improve endurance exercise capacity in young healthy volunteers
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of acute and 4-week Rhodiola rosea intake on physical capacity, muscle strength, speed of limb movement, reaction time, and attention.
Conclusion: Acute Rhodiola rosea intake can improve endurance exercise capacity in young healthy volunteers. This response was not altered by prior daily 4-week Rhodiola intake.
Acute Rhodiola Rosea Intake Can Improve Endurance Exercise Performance, Katrien De Bock, Bert O. Eijnde, nternational journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 2004 14
Quantification of polyherbal formulations containing Rhodiola rosea
The analyses revealed that the quality issue of commercial R. rosea extracts was a big concern because the characteristic bioactive compounds, i.e. rosarin, rosavin and rosin of R. rosea were not detected in 33.3% of the commercial R. rosea extract samples tested.
Abstract : An RRLC method capable of simultaneous identification and rapid quantification of six biologically active compounds (salidroside, tyrosol, rosarin, rosavin, rosin, rosiridin) in Rhodiola rosea L. and two active compounds (eleutheroside B and eleutheroside E) in Eleutherococcus senticosus Maxim. was developed. The chromatographic analyses were performed on a reversed phase Phenomenex C18 (2)-HST column at 40 ◦C with a neutral mobile phase (purified water and acetonitrile) gradient system at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min and UV detection at 205 and 220nm simultaneously. Baseline separation of eight active compounds was achieved within 8 min. This developed method provides good linearity (R min 0.9997), precision (RSD max 1.99%) and recovery of the bioactive compounds. The RRLC method developed is capable of controlling the quality of R. rosea and E. senticosus raw herbs, commercial extracts, as well as polyherbal formulations containing R. rosea and E. senticosus as ingredients. This RRLC method is accurate and sensitive; in addition, it greatly increases sample analysis throughput with reduced analysis time, which is suitable for routine quality control analysis.
Discussion : R. rosea and E. senticosus are two of the most extensively studied adaptogens in both pharmacological and clinical studies. In the present study, we have successfully developed an RRLC method to control the quality of commercial formulated products which contain R. rosea and E. senticosus components. This RRLC method is capable of simultaneously analyzing six biological compounds, i.e. salidroside, tyrosol, rosarin, rosavin, rosin, rosiridin in R. rosea and two biological compounds, i.e. eleutheroside B and eleutheroside E in E. senticosus with high resolution in a single run within 8min. Additionally, this method was fully validated with respect to precision, repeatability and accuracy.
This method allows strict quality control not only for raw material R. rosea and E. senticosus extracts, but also for commercial polyherbal formulated products. The analyses revealed that the quality issue of commercial R. rosea extracts was a big concern because the characteristic bioactive compounds, i.e. rosarin, rosavin and rosin of R. rosea were not detected in 33.3% of the commercial R. rosea extract samples tested. Furthermore, there was also a big variation between the actual rosavins content and the amount claimed by suppliers. No deviation was observed in the five batches of commercial E. senticosus extracts quantitatively. This method was further applied to analyze six samples of commercial polyherbal formulated capsules collected on the market that contain R. rosea and E. senticosus ingredients.
Simultaneous quantification of polyherbal formulations containing Rhodiola rosea L. and Eleutherococcus senticosus Maxim. using rapid resolution liquid chromatography (RRLC), Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 55 (2011) 908–915, Yuan-Chun Ma, Xiao-Qiang Wang, FeiFei Hou, Jie Ma
Antinociceptive And Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rhodiola Rosea
The studied extract of Rhodiola rosea exhibited significant analgesic activity in all the pain models used – inhibition of thermal pain, mechanical hyperalgesia and formalin-induced pain behavior. Significant anti-inflammatory activity was observed from Rhodiola rosea extract in carrageenan induced paw edema in rats
BACKGROUND: Rhodiola rosea (golden root) is a unique phytoadaptagen with immunomodulatory, antioxidant, anti-infl ammatory and antinociceptive activity. AIM: The aim of this study was to evaluate the antinociceptive and anti-infl ammatory effects of the alcohol/water extract of Rhodiola rosea roots in rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty male Wistar rats were used in the study. They were divided in 3 groups (n = 10), treated respectively with saline (controls), Rhodiola rosea extract 50 mg/kg bw and 100 mg/kg bw orally. The antinociceptive effect was evaluated using the hot-plate test, Randall-Sellito test and the formalin test. The hot-plate test evaluates the reaction time of rats which are dropped on a heated surface. The analgesy-meter test exerts a force increased at constant rate. In the formalin test we measured the total time spent in licking the injected paw during the early (0-10 min) and late phase (20-30 min) of test. To study anti-infl ammatory effect the carrageenan-induced paw edema was used. The paw volume was measured plethysmometrically at 2, 3 and 4 hours.
RESULTS: In the hot-plate test Rhodiola rosea increased in both doses the latency reaction compared with that in the controls. In analgesy-meter test Rhodiola rosea in a dose of 50 mg/kg showed a signifi cant increase of pressure reaction compared with the controls. In the formalin test Rhodiola rosea in a dose of 100 mg/kg signifi cantly decreased the paw licking time during the fi rst phase. In the plethysmometer test Rhodiola rosea extract signifi cantly reduced carrageenan-induced paw edema when compared with the saline-induced edema.
CONCLUSION: The studied extract of Rhodiola rosea exhibited significant analgesic activity in all the pain models used – inhibition of thermal pain, mechanical hyperalgesia and formalin-induced pain behavior. Significant anti-inflammatory activity was observed from Rhodiola rosea extract in carrageenan induced paw edema in rats.
Antinociceptive And Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rhodiola Rosea L. Extract In Rats, Nina D. Doncheva, Anita St. Mihaylova, Damianka P. Getova, Folia Medica 2013; 55(3&4): 70-75
Traditional Herbal Medicines for Modern times
Traditional Herbal Medicines for Modern Times, Rhodiola rosea, Edited by Alain Cuerrier, Kwesi Ampong-Nyarko
Chapter 1 Taxonomy of Rhodiola rosea L., with Special Attention to Molecular Analyses of Nunavik (Québec) Populations, Alain Cuerrier, Mariannick Archambault, Michel Rapinski, and Anne Bruneau
Chapter 2 Ethnobotany and Conservation of Rhodiola Species, Alain Cuerrier, Youri Tendland, and Michel Rapinski
Chapter 3 Phytochemistry of Rhodiola rosea, Fida Ahmed, Vicky Filion, Ammar Saleem, and John T. Arnason
Chapter 4 Cultivation of Rhodiola rosea in Europe, Bertalan Galambosi
Chapter 5 Rhodiola rosea Cultivation in Canada and Alaska, Kwesi Ampong-Nyarko
Chapter 6 Diseases of Wild and Cultivated Rhodiola rosea, Sheau-Fang Hwang, Stephen E. Strelkov, Kwesi Ampong- Nyarko, and Ron J. Howard
Chapter 7 Biotechnology of Rhodiola rosea, Zsuzsanna György
Chapter 8 Pharmacological Activities of Rhodiola rosea, Fida Ahmed, Steffany A.L. Bennett, and John T. Arnason
Chapter 9 Evidence-Based Efficacy and Effectiveness of Rhodiola SHR-5 Extract in Treating Stress- and Age-Associated Disorders, Alexander Panossian and Georg Wikman
Chapter 10 Rhodiola rosea in Psychiatric and Medical Practice, Patricia L. Gerbarg, Petra A. Illig, and Richard P. Brown
Chapter 11 Toxicology and Safety of Rhodiola rosea, Hugh Semple and Brandie Bugiak
Chapter 12 Commercialization of Rhodiola rosea, Nav Sharma and Raimar Loebenberg
Antioxidant Activity towards Xanthine Oxidase Lipoxygenase Tyrosinase
Koelreuteria henryi, Prunus campanulata, and Rhodiola rosea showed the highest xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. Camellia sinensis, Rhodiola rosea, and Koelreuteria henryi exhibited good tyrosinase inhibitory activities and potent anti-lipoxygenase activities.
Abstract: Natural products have the potential to be developed into new drugs for the treatment of various diseases. The aim of the present study was to screen the antioxidant activities of some common edible fruits, garden plants and medicinal plants indigenous to Taiwan. This was performed by assessing the activities of lipoxygenase, xanthine oxidase and tyrosinase following incubation with extracts from these plants. A further aim was to use HPLC-DAD and tyrosinase to chromatographically identify the antioxidative constituents obtained from an extract exhibiting strong antioxidative properties. The acetone extracts of 27 cultivated plant species from Taiwan were tested for antioxidant activities towards xanthine oxidase, tyrosinase and lipoxygenase using spectrophotometric assays. Koelreuteria henryi, Prunus campanulata, and Rhodiola rosea showed the highest xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. Camellia sinensis, Rhodiola rosea, and Koelreuteria henryi exhibited good tyrosinase inhibitory activities and potent anti-lipoxygenase activities. As Koelreuteria henryi had notable significant inhibitory activities towards xanthine oxidase, tyrosinase, and lipoxygenase, it was further tested with tyrosinase and HPLC-DAD. The results from this part of the study revealed that the more powerful the antioxidant capability of the extracted component, the greater the decrease in peak height obtained after reacting with tyrosinase. Additional studies are warranted to further characterize the compounds responsible for the antioxidant properties of the examined extracts.
Keywords: HPLC-DAD; antioxidant; plant extracts; xanthine oxidase; tyrosinase; lipoxygenase
Antioxidant Activity of Some Plant Extracts Towards Xanthine Oxidase, Lipoxygenase and Tyrosinase, Chin-Hui Chen, Hsiu-Chen Chan, Yi-Tsu Chu, Molecules 2009, 14, 2947-2958
Rhodiola : Nature’s Energy Booster
While the world of today shows no signs of slowing down, adults can bolster their ability to respond to daily stressors—both mental and physical—by using rhodiola extract. Given its vast potential for averting stress-related disorders, this remarkable herb from the Arctic regions of Russia has no doubt found a lasting place in the medicine cupboards of forward-thinking consumers today.
A unique herbal remedy, rhodiola grows and thrives in dry, sandy ground at high altitudes in Arctic areas of Europe and Asia. Soviet scientists have long known that this native herb—particularly the species known as Rhodiola rosea—can boost energy and treat mental fatigue, along with other conditions. Now that the Cold War has ended, so have the barriers to our knowledge of rhodiola’s benefits. News about this versatile herb is spreading around the world, prompting scientists to take a closer look at the herb’s many applications. Their new findings confirm the multiple physiological and psychological benefits of rhodiola, demonstrating that the herb indeed offers a powerful antidote to the stresses of modern-day life.
Improving the Body’s Response to Stress Stress is an inevitable fact of life, but it can have serious consequences on our mental and physical health. Effective strategies for managing stress are therefore essential to thrive in a fast-paced world. Research suggests that rhodiola may offer a practical, natural solution for overcoming many stress-related complaints .It is believed that rhodiola enhances the body’s tolerance to stress by influencing key brain chemicals, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, and natural feel-good opioids such as beta-endorphins.
Also in this article :
- Enhancing Nervous System Health
- Boosting Physical Endurance
- New Research Highlights Diverse Benefits
- Integrative Practitioners Praise Rhodiola’s Benefits
- Using rhodiola : The average dose of R. rosea is between 200 mg and 400 mg per day of an extract that is standardized to contain rosavins and salidrosides in a 3:1 ratio. This mimics the ratio of these compounds that naturally occur in R. rosea root
Nature’s Energy Booster by Peter Broatto - Rhodiola is a unique herbal remedy
Nektium : committed to a sustainable future
Our partner Nektium has just published its sustainability report, highlighting its initiatives and commitments in terms of environmental and social responsibility.
CITES approval of stock for Rhodiola Rhodiolife®
The regulatory framework within the EU was updated from annex D to annex B - after a delay of almost 2 months compared to the rest of the world - and we are now happy to inform you that the corresponding permits for Nektium were issued.
BECARRE Natural invites you to join us at Vitafoods Europe 2023, 09-11 May in Palexpo, Geneva
As every year, you will be welcome to meet us during Vitafoods 2023. Our wide range of standardized and objectivized plant extracts will be on display at stand J170, Pavillon France.
Nektium takes steps to ensure the long-term sustainability of its Rhodiola rosea extract Rhodiolife®
Pioneering cultivation program boosts adaptogen sustainability
Rhodiolife® stimulates and protects the immune system
The Rhodiola extract Rhodiolife® has clearly demonstrated its ability to protect cells from viral infection.
Are you interested in our solutions and want to know more?
Becarre Natural represents, distributes and develops natural actives extracts from plants for nutrition health and cosmeceutical.
Contact us